The Work and Applications of Geonet in Construction
Geonets are a silent but crucial player in the world of construction, offering a myriad of innovative solutions for drainage, erosion control, and soil stabilization. Geonets, three-dimensional grid-like structure, typically composed of high-density polyethylene or polypropylene, paves the way for efficient fluid flow and soil reinforcement. In geonet application work, these geosynthetic marvels excel at channeling water away from critical infrastructure, ensuring roads and embankments remain resilient against moisture-related damage. Geonets also serve as protectors against erosion, preventing soil loss and safeguarding slopes from landslides. Whether used in landfill liners, retaining walls, or pavement reinforcement, geonets are essential for preserving the integrity and longevity of construction projects, making them indispensable in today’s modern construction landscape.
What is a geonet?
A geonet is a geosynthetic material consisting of integrally connected parallel sets of ribs overlying similar sets at various angles for in-plane drainage of liquids or gases. Typically crafted from polymer materials, such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene, geonets are designed with a three-dimensional structure that resembles a net or grid. This unique structure allows for the efficient passage of fluids, making geonets particularly useful in drainage and filtration applications.
What is a GeoNet made of?
Geonets are typically made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene materials. These polymers are woven or extruded to create a three-dimensional, grid-like structure. The specific composition and design may vary depending on the intended application and manufacturer, but the fundamental purpose of geonets remains consistent: efficient drainage and erosion control.
What are the applications of geonet?
Geonets find a wide array of applications in construction and civil engineering projects, including road construction, road widening, and asphalt work, building construction and foundations, retaining walls, dams, artificial ponds, water reservoirs, and many more. Some of the primary uses include:
- Drainage: Geonets excel in subsurface drainage applications, facilitating efficient water flow and soil consolidation. This is crucial for maintaining the stability and performance of the project.
- Erosion Control: Geonets prevent soil erosion by stabilizing the soil, especially in sloped or hilly terrains. They create a protective layer against rainfall and surface water flow, reducing the risk of landslides and washouts.
- Landfill and Pond Liners: Geonets are used in landfill and pond liner systems to provide drainage paths, separating the liner material from the soil. This helps prevent the accumulation of leachate, preserving the integrity of the liner and the environment.
- Retaining Walls: Geonets can be employed in retaining wall structures to enhance drainage, reduce hydrostatic pressure, and improve wall stability. They add an extra layer of protection and durability to such structures
What is the difference between geogrid and geonet?
While both geonets and geogrids are geosynthetic materials, they serve different purposes and have distinct structures. Geogrids are two-dimensional materials, often made from polyester or polypropylene, designed to reinforce and stabilize soil. They are commonly used in applications like road reinforcement, retaining walls, and embankment stabilization.
Geonets, on the other hand, are three-dimensional materials designed primarily for drainage, filtration, and erosion control. Their grid-like structure facilitates the efficient flow of fluids while also providing support against soil erosion.
What is the use of geonet in road construction?
In road construction, geonets play a pivotal role in enhancing the longevity and performance of the road infrastructure. They are used for:
- Subsurface Drainage: Geonets efficiently channel water away from the road structure, providing reinforcement, stabilization, and filtration. This prevents water infiltration and maintains the road’s integrity, which is critical in preventing moisture-related damage and extending the road’s lifespan.
- Erosion Control: Geonets stabilize the soil, reducing the risk of erosion in areas with challenging terrain, providing both reinforcement and stabilization. This helps prevent landslides and washouts.
- Slope Stabilization: Geonets are employed on road embankments and slopes to prevent soil erosion and maintain the stability of these areas, offering reinforcement and stabilization.

In conclusion, geonets are versatile geosynthetic materials that find applications across various construction projects. Their ability to manage drainage, control erosion, and enhance soil stability makes them a valuable asset in the construction industry, particularly in road construction and environmental protection. Understanding the differences between geonets and geogrids is crucial for selecting the right material for specific project requirements.
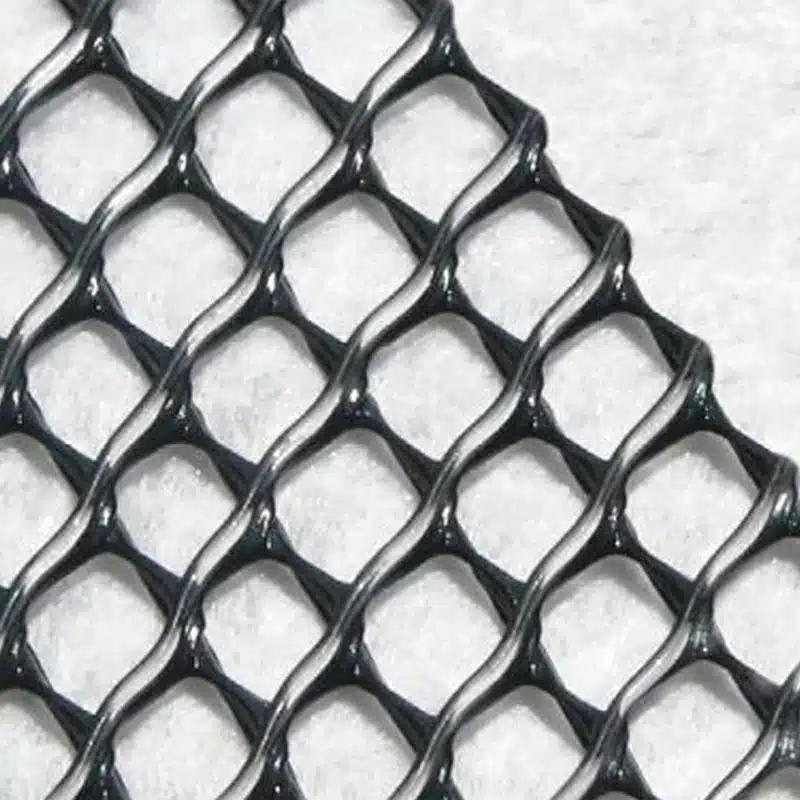
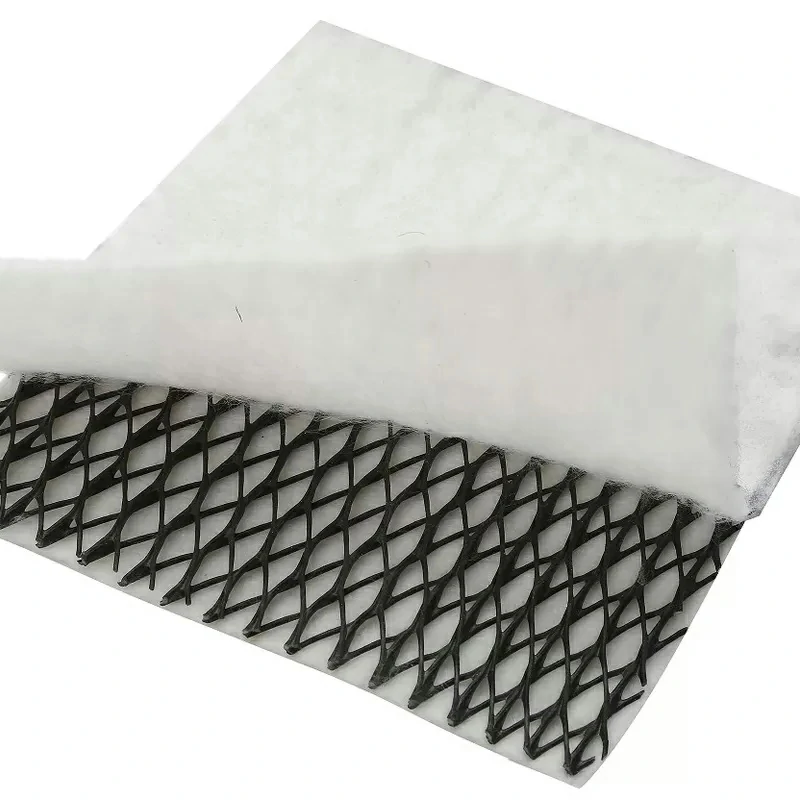


Comments
Post a Comment