When to Install Geogrid: A Crucial Decision in Construction
When to install geogrid is a question that often determines the success and longevity of construction projects. Geogrids, powerful geosynthetic materials, play a pivotal role in bolstering the stability of various structures, including retaining walls, roads, and embankments. The decision to use geogrids hinges on several factors, such as soil conditions, slope stability, and load-bearing requirements. Weak soils, steep slopes, and areas where foundation support is compromised are all situations that demand geogrid reinforcement. The judicious use of geogrids not only enhances structural integrity but also leads to cost savings and extended lifespans for your construction endeavors. In the world of construction, understanding when to install geogrid is a vital step toward building durable, safe, and reliable infrastructure.

When should geogrid be used?
Geogrids should be considered in the following situations:
- Weak Soil Conditions: When the native soil lacks the necessary load-bearing capacity, geogrids provide reinforcement by distributing and dissipating loads effectively.
- Slope Stabilization: Geogrids play a crucial role in stabilizing slopes, especially on steep inclines, and preventing soil erosion.
- Road Construction: Geogrids improve the performance and longevity of roads by distributing the load and reducing the risk of rutting.
- Retaining Walls: Geogrids are commonly used to reinforce retaining walls, ensuring they withstand lateral earth pressures, particularly in cases involving walls taller than three to four feet.
- Foundation Support: In construction projects where foundations are placed on soft soils, geogrids enhance the foundation’s stability.
When should you use geogrids rather than geotextile?
Geogrids, primarily used for soil reinforcement, and geotextiles serve different purposes:
- Geogrids: Choose geogrids when structural reinforcement and load distribution are needed. They are perfect for applications where tensile strength and stiffness are essential, such as retaining walls, embankments, and roadways.
- Geotextiles: Geotextiles are primarily employed for filtration, separation, and erosion control. They are well-suited for applications like drainage systems, underneath roads, and landscaping to prevent soil erosion.
Why do you need Geogrid?
Geogrids are indispensable for several critical purposes, including slope stabilization, soil stabilization, and soil reinforcement:
- Enhanced Stability: Geogrids are instrumental in soil reinforcement, preventing settlement, and maintaining structural integrity.
- Cost Savings: Geogrids bolster weak soils, reducing the necessity for excessive excavation or imported fill material, resulting in substantial cost savings.
- Extended Lifespan: Geogrids enhance the longevity of structures such as retaining walls and roads, minimizing maintenance and repair costs.
- Safety: Geogrids are a crucial component in reducing the risk of slope failures, landslides, and other soil-related hazards.
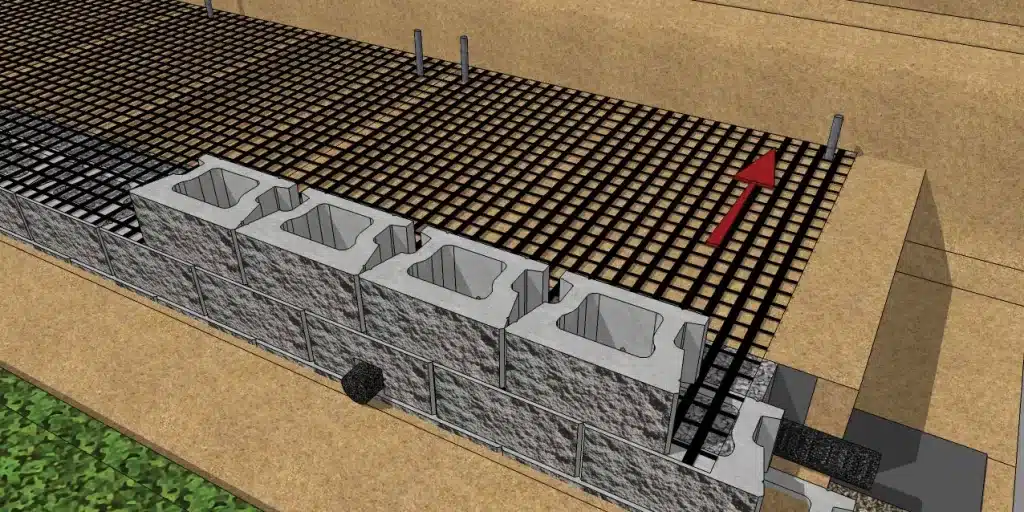
Where are geogrids used?
Geogrids find reinforcement applications in various types of construction projects but can be used for separation applications as well, including:
- Retaining Walls: Geogrids provide support and stability to retaining walls, preventing them from collapsing under the pressure of the retained soil.
- Road Construction: They are used in road bases to improve load-bearing capacity and reduce rutting.
- Slope Stabilization: Geogrids are essential in preventing soil erosion and maintaining the integrity of slopes.
- Foundation Support: For buildings and structures on weak or expansive soils, geogrids enhance foundation support.
- Embankments: In transportation projects, geogrids are used to reinforce embankments, reducing settlement.
Can you build a retaining wall without geogrid?
While it’s technically possible to build a retaining wall without geogrid, doing so may not be wise. Retaining walls without geogrid are generally suitable for small, low walls. However, for taller walls or walls retaining substantial loads, geogrids are strongly recommended to enhance stability and prevent wall failure. Once the retaining wall is over 6′ in height if it isn’t being built from 24″+ wide limestone outcroppings or similarly sized, dense material, geogrid is required. In the interest of long-term safety and structural integrity, it is advisable to use geogrids in most retaining wall projects.
Comments
Post a Comment