Maximizing Geonets Performance in Construction: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to construction and geotechnical projects, achieving superior geonet performance is paramount for effective moisture management and ensuring the structural integrity of engineered structures. Geonets, with their intricate designs and efficient drainage capabilities, play a vital role in redirecting water away from critical areas. Their exceptional drainage efficiency ensures that moisture is managed effectively, reducing the risk of hydrostatic pressure buildup, particularly in underground applications like tunnels and basements. Geonets also enhance soil stability and prevent erosion, making them an ideal choice for slope stabilization and embankment construction. By selecting the right Geonet materials and employing appropriate installation methods tailored to the specific project requirements, you can optimize Geonets’ performance and extend the longevity of your construction projects while minimizing labor and transportation costs.
What is the importance of geonets?
The Benefits of Geonets
Geonets are invaluable elements in construction and geotechnical projects, primarily due to their exceptional drainage performance, which plays a crucial role in reducing labor and transportation costs. They efficiently divert water away from critical areas, ensuring efficient moisture management. This, in turn, not only safeguards the structural integrity of projects, particularly in underground applications like tunnels and basements by mitigating the accumulation of hydrostatic pressure but also leads to cost savings by reducing labor and transportation costs. Furthermore, geonets bolster soil stability and prevent erosion, making them the go-to choice for slope stabilization and embankment construction while contributing to significant cost reductions in labor and transportation expenses.
What is the difference between geogrids and geonets?
While geonets and geogrids are both geosynthetic materials used for soil reinforcement, they serve distinct purposes and have different structures.
- Geogrids are two-dimensional with a grid-like structure, primarily employed for soil reinforcement and stabilization, particularly in applications like road construction and retaining walls. Their focus lies in enhancing the tensile strength of the soil.
- Geonets are three-dimensional with open channels, primarily used for drainage and moisture management in various applications. Geonets excel at controlling water flow and reducing pressure buildup, making them suitable for situations where effective drainage is critical.
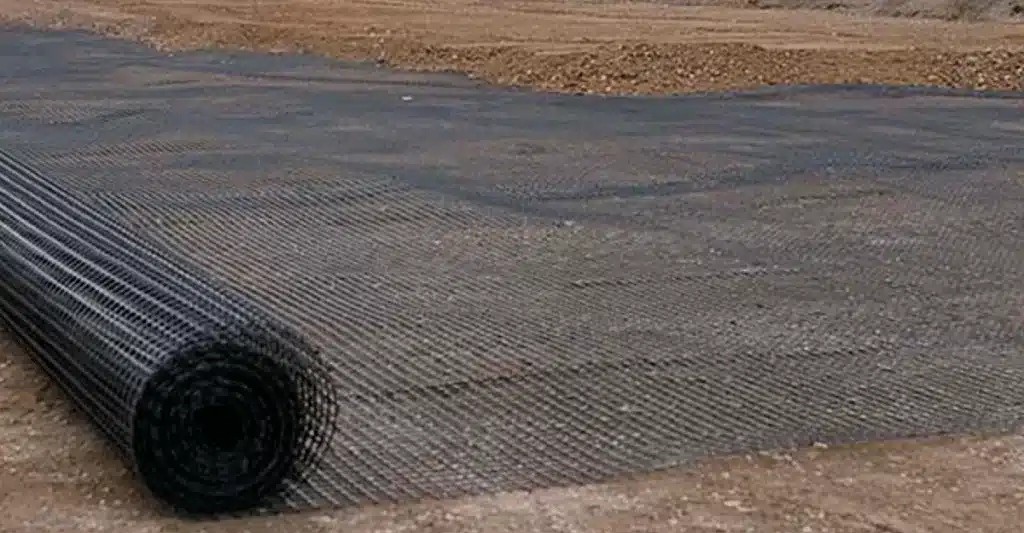

What are the properties of geonets?
Geonets possess several essential properties, making them invaluable in construction and geotechnical projects. These properties include their intricate design, efficient drainage capabilities, lightweight nature, and durability. Their grid-like structure features integrally connected parallel sets of ribs, creating open channels for water flow, and showcasing their “High flow capacity.” Geonets are known for their longevity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation, which not only benefits the project but also reduces both labor and transportation costs. Moreover, they are available in various sizes, thicknesses, and materials, allowing them to be tailored to meet specific project requirements.
What are the applications of geonet?
Geonet Application:
- Landfill cells.
- Hydraulic.
- Transportation Engineering.
- Road, Rail, Highways, and Tunnel.
- Environmental.
- Garden and Playground.
- Parking Lot.
- Geotechnical.
Geonets find applications in a wide range of construction and geotechnical projects. They are particularly valuable in retaining walls, landfills, green roofs, tunnels, basements, and embankment construction. Geonets offer versatile solutions for efficient moisture management, drainage, and soil stabilization. Their flexibility in design and material options makes them suitable for a variety of projects.
What is the use of geonet in road construction?
In road construction, geonets play a pivotal role in enhancing the structural integrity of roadways and improving their long-term performance. They effectively manage moisture and control water flow beneath the road surface, which not only reduces the risk of subsurface erosion and instability but also helps improve the strength and stability of subgrade soils, extending the lifespan of roads and reducing maintenance costs. This becomes especially crucial in areas with high water tables or frequent rainfall. Additionally, geonets aid in mitigating the impact of frost heave, a common issue in cold climates, by providing a drainage path for excess water, preventing the expansion of freezing soil that can damage roads. Overall, the utilization of geonets in road construction contributes to safer, more durable, and cost-effective infrastructure while concurrently improving the strength and stability of subgrade soils, which leads to extended road lifespans and reduced maintenance expenses.


Comments
Post a Comment