The transmissivity of geocomposite drainage is a fundamental concept that plays a pivotal role in the field of geotechnical engineering. It measures the ability of geocomposite drainage materials to facilitate the flow of fluids, particularly water. This parameter is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of these materials in various geotechnical applications such as drainage, filtration, and containment. Understanding the transmissivity of geocomposite drainage materials is crucial for selecting the right material to ensure efficient water management and the successful execution of geotechnical projects. Engineers and designers rely on this knowledge to make informed decisions that can impact the overall performance and functionality of their projects, from mitigating waterlogging to ensuring soil stability and containment system integrity.
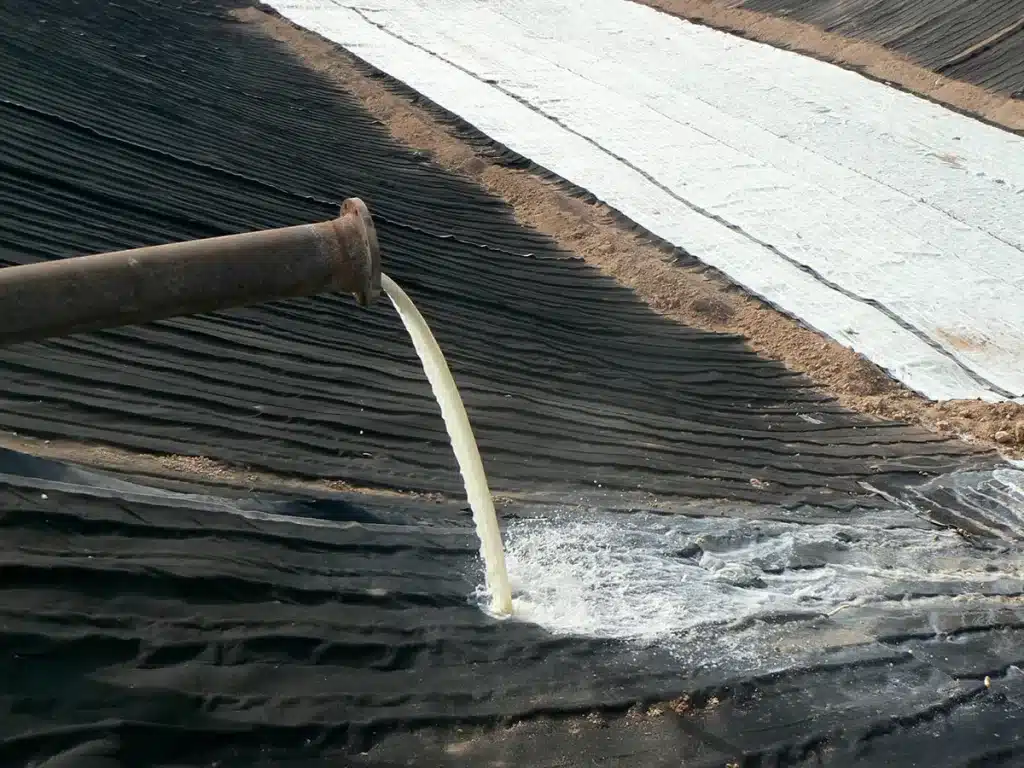

What is the flow rate transmissivity?
Flow rate transmissivity is a fundamental property that gauges the capacity of a material to transmit fluids, usually water. It quantifies the volume of fluid that can pass through a unit area of the material under a unit hydraulic gradient, which signifies the rate at which groundwater can flow through an aquifer section of unit width under a unit hydraulic gradient. In the context of geocomposite drainage, flow rate transmissivity assumes critical significance as it directly influences the system’s proficiency in efficiently draining excess water.
What is the transmissivity of geonet?
Geonets, with their distinct transmissivity values, are frequently employed components in geocomposite drainage systems. Geonet transmissivity, often quantified as “1.0×10^3 m²/sec,” measures the geonet’s capability to transmit water through its structure. Geonets are ingeniously designed with unique profiles that establish flow channels, enabling water to move swiftly and efficiently within the drainage layer. A higher transmissivity value in geonets directly corresponds to enhanced drainage performance, ensuring a more effective and efficient management of water.
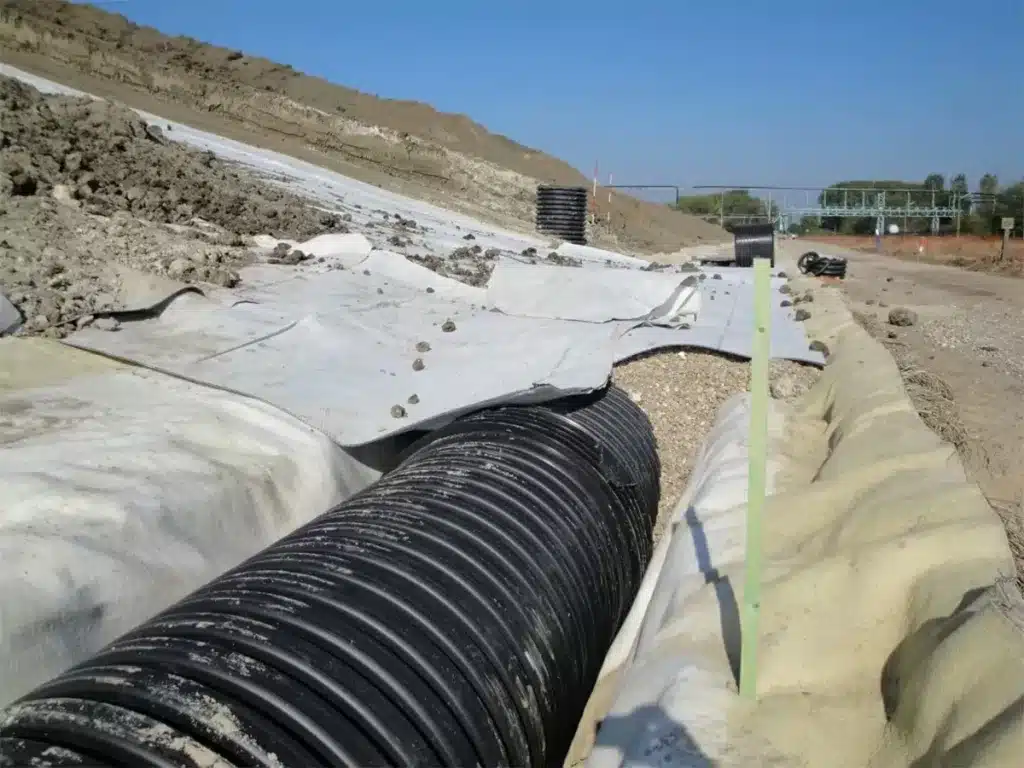

What is the transmissivity of geosynthetics?
Transmissivity in geosynthetics, more expansively, pertains to the capacity of various geosynthetic materials, encompassing geonets, geotextiles, and geomembranes, to enable the flow of fluids. This encompasses evaluating transmissivity as “the product of the permeability of the geotextile for in-plane water flow and the thickness of the geotextile.” Geosynthetics are meticulously selected and engineered for specific applications, making it imperative to comprehend their transmissivity values. This knowledge is pivotal in the selection of the most suitable material to guarantee effective drainage, filtration, or containment, aligning the geosynthetic with the unique demands of each application.
How do you determine transmissivity?
Transmissivity, a key parameter in geotechnical analysis, can be ascertained through laboratory testing. A prevalent testing procedure encompasses fabricating a sample of the geocomposite drainage material, subjecting it to hydraulic pressure or a gradient, and quantifying the flow rate of water through the material. The outcome is quantified as a transmissivity coefficient, frequently represented as “T,” which is defined as “equal to the product of the aquifer thickness (m) and hydraulic conductivity (K),” with units of length squared per time (e.g., m²/s). This coefficient empowers engineers and designers with the means to effectively compare and select appropriate geocomposite materials tailored to their specific applications.
Why is transmissivity a crucial factor in geocomposite drainage design?
Transmissivity is a critical factor in geocomposite drainage design because it directly impacts the system’s performance and efficiency. When designing a drainage system for construction, landscaping, or environmental projects, the ability to efficiently remove excess water and prevent waterlogging or erosion is paramount. A higher transmissivity value ensures that the geocomposite drainage can effectively handle the expected flow rates, reducing the risk of water-related issues. Proper drainage helps maintain the structural integrity of infrastructure, improves soil stability, and prevents damage to the environment. Understanding and utilizing transmissivity values in design and material selection ensures that the geocomposite drainage system will meet the specific needs of the project, ultimately leading to better outcomes and long-term success.

Comments
Post a Comment