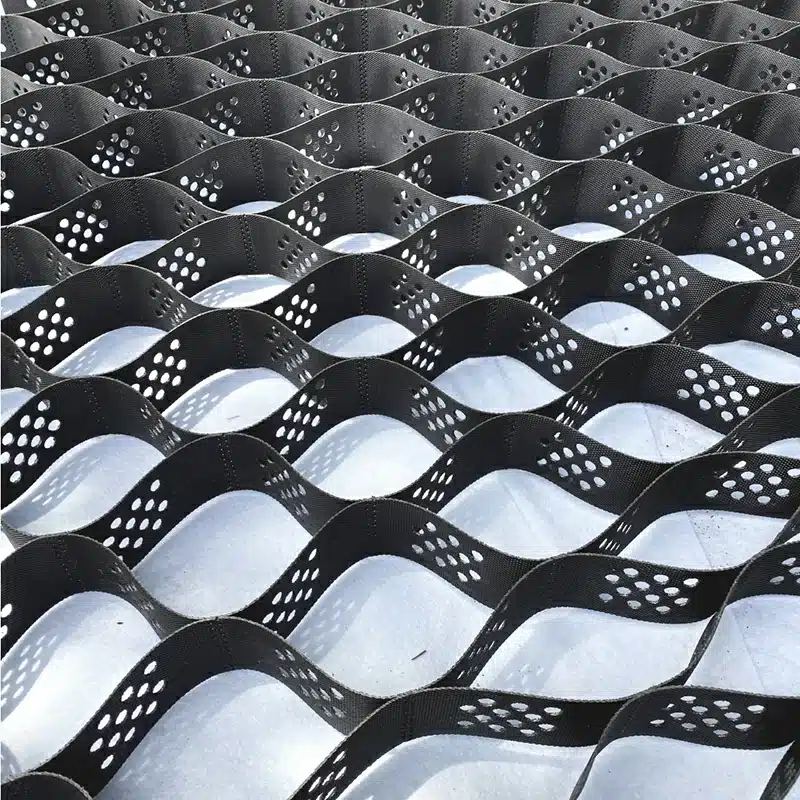
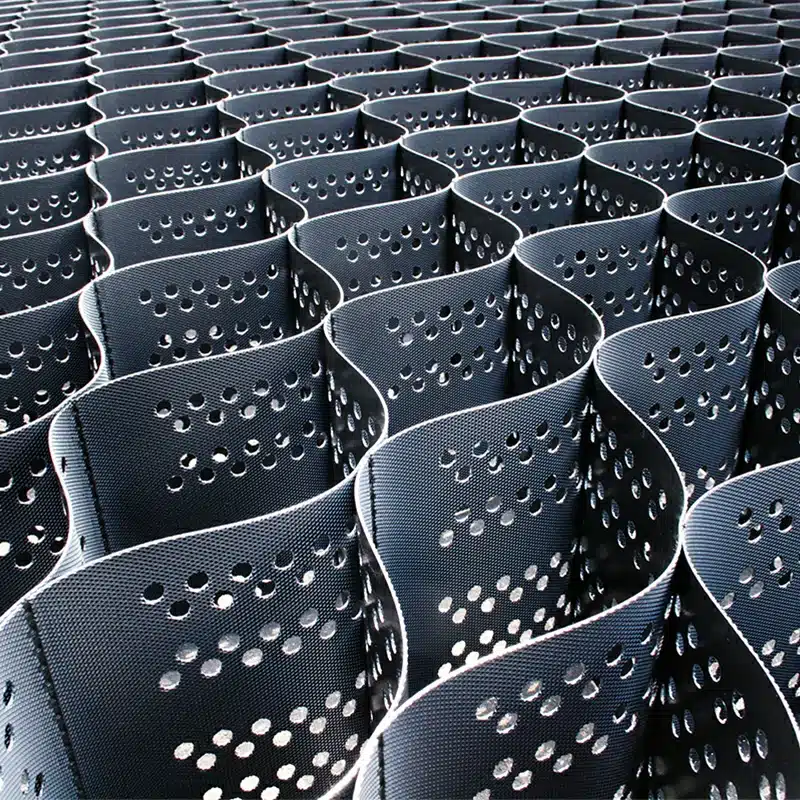
Maximizing Stability and Durability with Gravel Geocells
Gravel geocells revolutionize infrastructure reinforcement with their unparalleled stability and durability. These innovative cellular confinement systems excel in fortifying gravel, providing exceptional support for various applications. By securely containing and reinforcing gravel within their interconnected cells, gravel geocells enhance load-bearing capacity on flat ground and steep slopes alike. Whether for road construction, parking lots, driveways, or pathway reinforcement, the utilization of gravel geocells ensures a resilient and long-lasting solution, optimizing stability and durability in diverse projects.
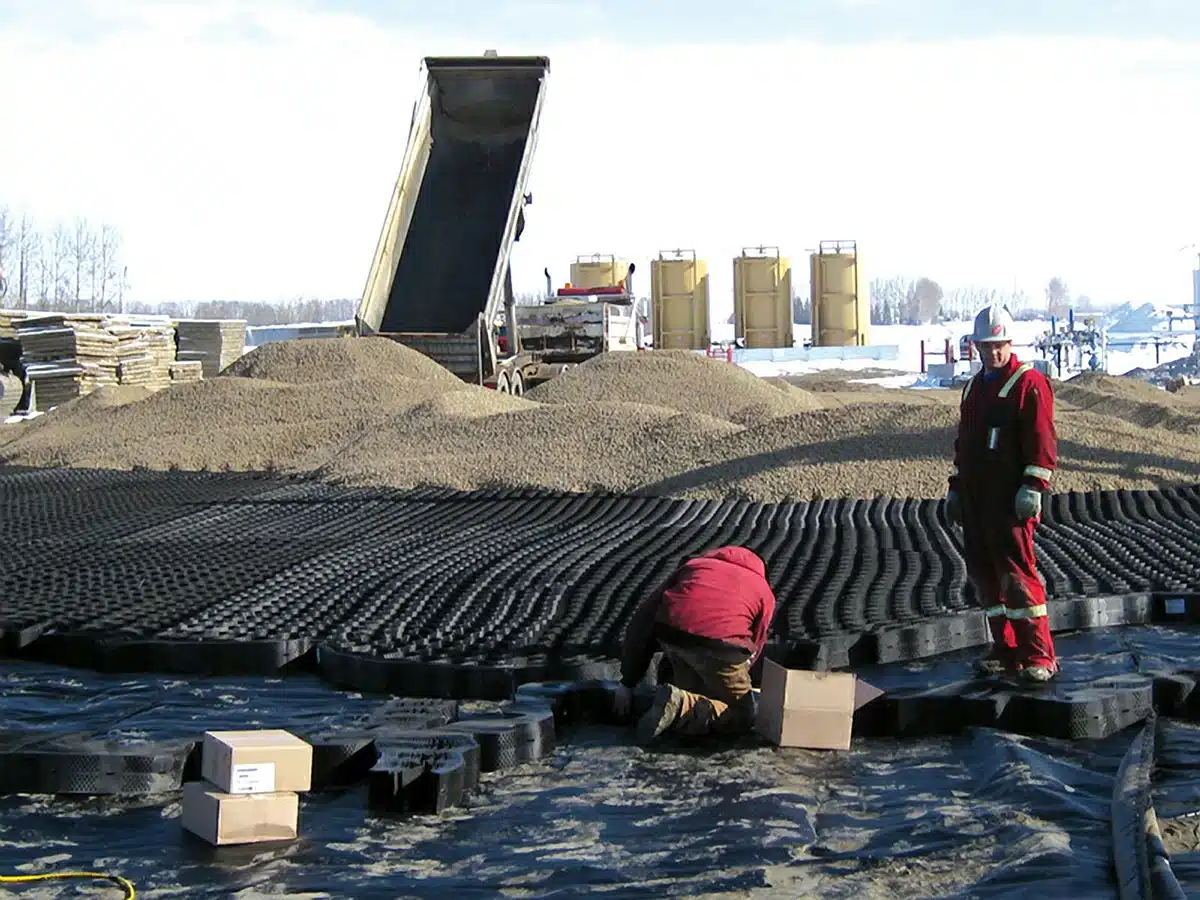

What is the best gravel for geocell?
Selecting the best gravel for geocells depends on several factors:
- Particle Size: Opt for angular gravel with uniform particle sizes between 3/8 to 3/4 inches, ensuring interlocking and stability within the geocell structure.
- Material Composition: Crushed stone or angular rock fragments are ideal choices due to their ability to interlock and distribute loads effectively.
- Durability: Choose gravel resistant to degradation and erosion, ensuring longevity and sustained performance within the geocell system.
- Compatibility: Consider gravel that complements the environmental conditions and load-bearing requirements of the intended project.
What is Geocell used for?
Geocells are versatile in their applications across different sectors, catering to:
- Soil Stabilization on Flat Ground and Steep Slopes: These cells effectively reinforce weak soils, offering solutions for erosion control and enhancing load-bearing capacities crucial for roads, embankments, and sloped areas.
- Gravel Stabilization: Geocells play a pivotal role in confining and supporting gravel, particularly in parking lots, driveways, and pathways. By doing so, they minimize surface rutting and bolster structural integrity.
- Erosion Control, Channel Protection, and Structural Reinforcement: In slope applications, geocells serve to mitigate erosion, ensuring stability, soil retention, and safeguarding the landscape’s integrity. Furthermore, they provide structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention, offering comprehensive solutions for erosion control and channel protection.
What is the difference between a geocell and a geogrid?
While both aid in soil stabilization, they differ in structure and application:
- Structure: Geocells consist of interconnected cells resembling a honeycomb, confining materials within them. Geogrids are flat, grid-like sheets made of polymeric materials.
- Functionality: Geocells primarily confine materials like gravel or soil, enhancing load distribution and erosion control. Geogrids provide reinforcement by distributing loads over a wider area and preventing soil movement.
What do you put under gravel grids?
For optimal performance and durability, it’s advisable to incorporate a non-woven geotextile membrane beneath gravel grids. This specialized membrane serves as a crucial separator, effectively preventing the intermingling of gravel with the underlying soil. Its primary functions include minimizing weed growth, facilitating superior drainage, and ensuring structural integrity over time.
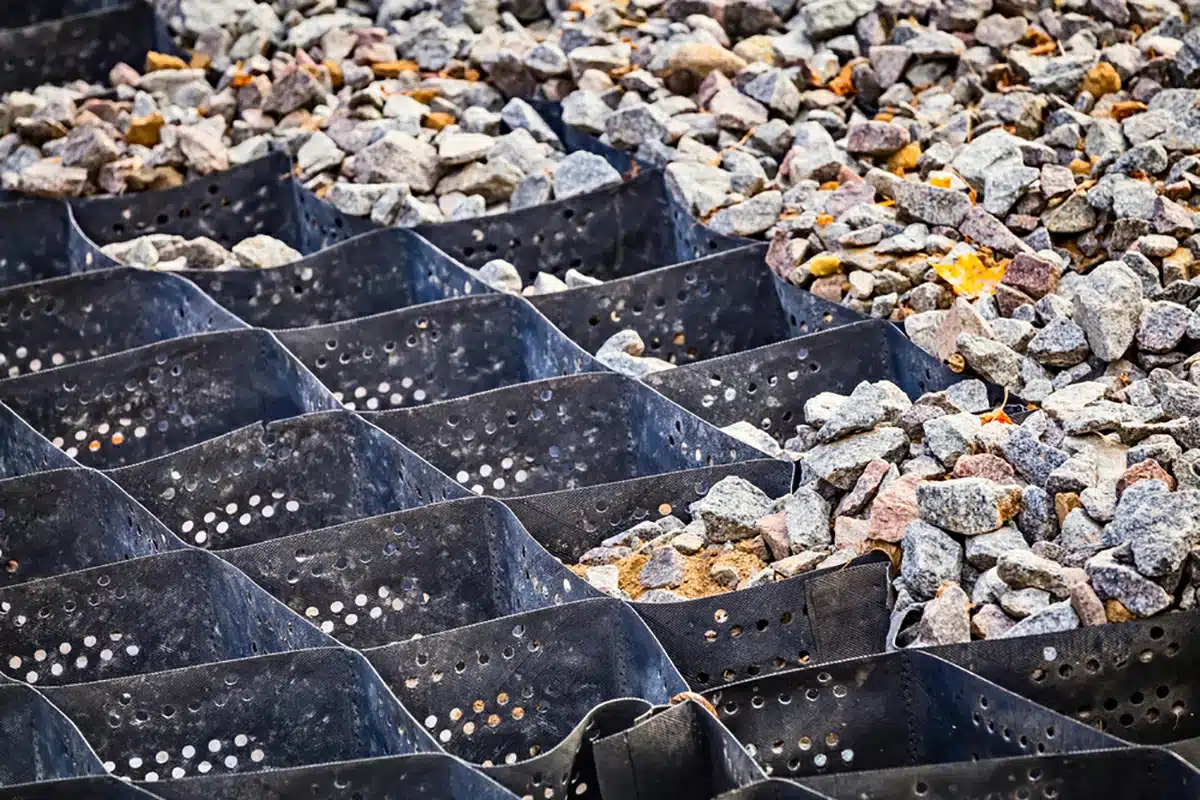

In conclusion, the synergy between geocells and the choice of gravel significantly impacts the efficiency and durability of infrastructure projects. By understanding the ideal gravel characteristics, coupled with the diverse applications of geocells, engineers and project managers can maximize the performance and longevity of their construction endeavors.

Comments
Post a Comment