Enhancing Stability with Geogrid: The Future of Block Retaining Walls
In the realm of civil engineering and landscape architecture, the quest for durable, stable, and aesthetically pleasing retaining walls has led to the innovative use of geogrids. These synthetic materials are crucial in efforts to provide reinforcement to the unreinforced soil, working in tandem with traditional block retaining walls. This synergy not only enhances the structural integrity of soil but also significantly extends the lifespan of the constructed walls. This article delves into the essential role of geogrids in retaining wall applications, exploring their types, installation processes, and the significant benefits they offer, including their ability to stabilize slopes and prevent soil erosion effectively.

When should you use geogrid on a retaining wall?
Geogrids should be considered for use in a retaining wall project when there is a need for enhanced stability and strength, especially in areas prone to erosion or with poor soil conditions. They are particularly beneficial for walls taller than three to four feet, as these structures will retain a significant height of soil or are in locations that experience heavy rainfall or seismic activity. Additionally, geogrids are ideal for projects where long-term durability is a priority, as they significantly reduce the likelihood of wall failure.
What are the three types of geogrid?
- Uniaxial Geogrids: These are designed to stretch in one direction, making them ideal for slope stabilization and retaining walls where the primary stress is in a single direction. This category includes the specialized Triax® geogrids, which are part of a broader range of solutions that also encompass Uniaxial, Biaxial, Triaxial (Triax®), and Geogrid-Geotextile Composites, offering tailored support for various engineering needs.
- Biaxial Geogrids: These geogrids can stretch in two directions and are used in applications where equal strength is needed both longitudinally and transversely, such as in roadway and pavement construction. The versatility of products in this category, including Uniaxial, Biaxial, Triaxial (Triax®), and Geogrid-Geotextile Composites, ensures a comprehensive approach to addressing diverse engineering challenges.
- Triaxial Geogrids: With a multi-directional structure, triaxial geogrids offer enhanced stability and are suitable for a wide range of applications, including base reinforcement and soil stabilization for both retaining walls and embankments. Their unique design is part of a larger family of geosynthetic products, which includes Uniaxial, Biaxial, Triaxial (Triax®), and Geogrid-Geotextile Composites, providing a robust solution for complex engineering projects.
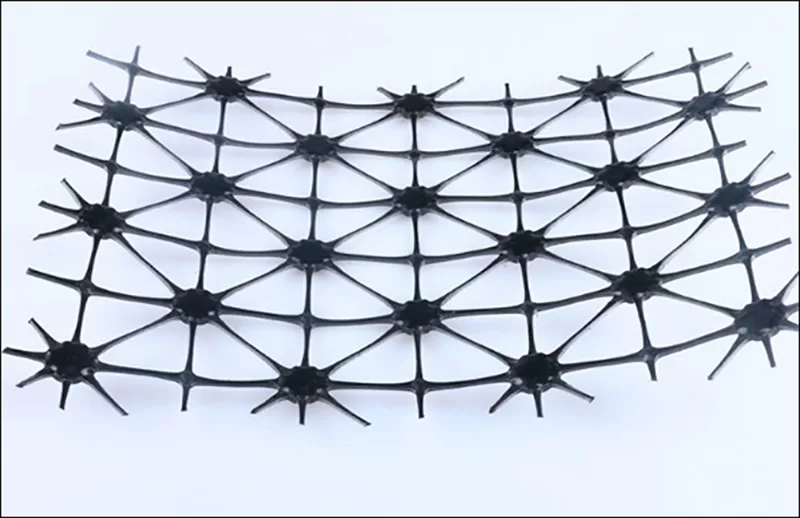
What is the lifespan of geogrid?
The lifespan of a geogrid can vary significantly based on the material composition, environmental conditions, and the specific application. However, most high-quality geogrids are designed to last for over 75 years, with some types made from durable polymers that can last about 100 years! The longevity of a geogrid is crucial for retaining walls, as it ensures that the structure remains stable and functional for decades with minimal maintenance, providing peace of mind and significant cost savings over time.
How is geogrid installed?
The installation of geogrid involves several key steps:
- Preparation of the Base: The area where the retaining wall will be built must be cleared and leveled. A solid foundation is critical for the stability of the wall.
- Building the Wall: As the block retaining wall is constructed, layers of geogrid are integrated at specified intervals. To ensure proper installation, simply roll it out and allow it to follow the natural contours of the ground, laying it out horizontally on the compacted soil behind the wall blocks.
- Backfilling: The space behind the wall is backfilled with soil, which is then compacted. The geogrid works by interlocking with this backfill material, creating a reinforced mass that acts together to resist the lateral pressure of the soil.
- Finishing Touches: After the wall reaches its desired height, and the final layer of geogrid is installed, a final backfill and compaction complete the installation process, ensuring the structure’s stability and longevity.
The integration of geogrid with block retaining walls represents a significant advancement in construction and landscaping. By understanding when and how to use geogrids, as well as the types available and their expected lifespan, professionals and homeowners alike can ensure the longevity and stability of their retaining walls. This innovative approach not only solves practical engineering challenges but also opens up new possibilities for aesthetic and functional landscape design.

Comments
Post a Comment