Understanding Geocomposite Price: An Insightful Guide
In the realm of civil engineering and construction, the use of innovative materials to solve traditional problems has become increasingly prevalent. Among these materials, geocomposites have emerged as a versatile and efficient solution for various applications. However, understanding the pricing of geocomposites requires a deep dive into what they are, their uses, and how they compare to similar materials like geotextiles. This article aims to shed light on geocomposite prices by exploring their differences from geotextiles, their applications, the types available, and the reasons for using geofabric, providing a comprehensive overview for professionals and enthusiasts alike.

What is the difference between geotextile and geocomposite?
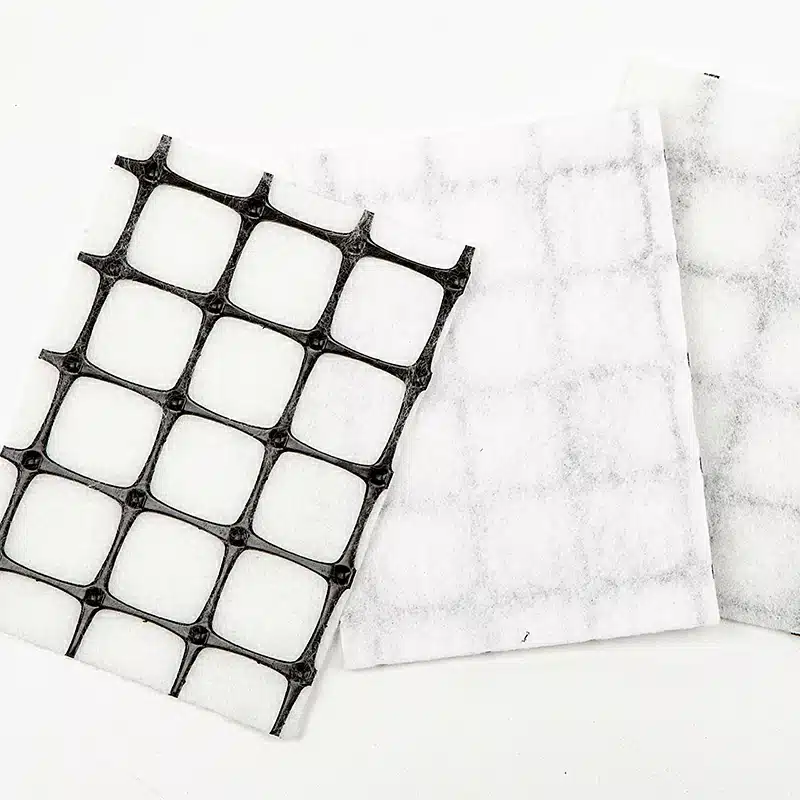
Geotextiles and geocomposites, while often mentioned in the same breath, serve different purposes and are composed of different materials. Geotextiles are permeable fabrics which, when used in association with soil, have the ability to separate, filter, reinforce, protect, or drain. On the other hand, geocomposites represent a more advanced category of materials. A geocomposite consists of a combination of one or more geosynthetics, specifically a geogrid, a geotextile, a geomembrane, and/or a geonet, with another material. This amalgamation creates a multifunctional product designed to offer a broader range of functions by leveraging the benefits of different materials. Consequently, the structure and functionality of geocomposites distinguish them from simpler geosynthetics like geotextiles. By integrating various geosynthetics, geocomposites are engineered to perform multiple roles, which can also influence their price, making them a versatile yet potentially more costly solution in geotechnical and environmental applications.
What are geocomposites used for?
Geocomposites are utilized across a broad spectrum of applications in the construction, environmental, and geotechnical engineering sectors, showcasing their versatility and multifunctionality. These applications encompass drainage in landfill caps and leachate management systems, gas venting systems, and waterproofing in tunnels and underground structures. Additionally, they play a crucial role in erosion control on slopes, and in road and railway construction for stabilization and reinforcement. Notably, geocomposites are also essential for drainage from a basal layer in case of embankments and for drainage behind retaining walls and/or bridge abutments, further underscoring their importance in ensuring structural integrity and longevity. The combination of properties such as filtration, separation, reinforcement, and drainage that geocomposites offer makes them a preferred choice for projects requiring a multifaceted approach to engineering challenges.
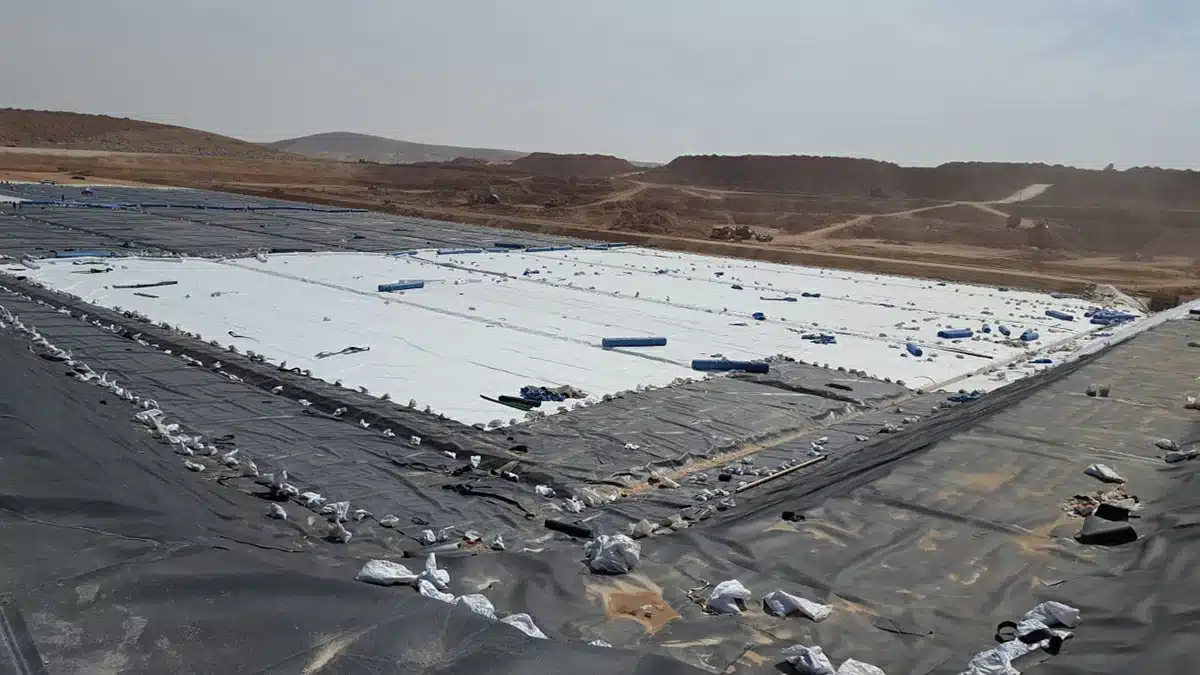

What are the different types of geocomposites?
You are a content editor. Please naturally integrate “drainage geocomposites, reinforcement geocomposites and fluid barrier geocomposites.” into the following paragraphs. The logic and semantics are smooth and the main idea of the paragraph remains unchanged:
There are several types of geocomposites available, each designed for specific applications and functionalities. These include:
- Geonet Composites: Designed for drainage, these consist of a geonet core with geotextiles on one or both sides.
- Geomembrane Composites: These combine a geomembrane layer with a geotextile or geonet for waterproofing and drainage applications.
- Geogrid Composites: Incorporating a geogrid layer, these are used for reinforcement in road and railway construction.
- Geosynthetic Clay Liners (GCLs): A type of geocomposite that combines geotextiles with bentonite clay, used primarily for sealing and containment in landfills and water bodies.
- Each type of geocomposite has its own price range, influenced by the complexity of its structure and the materials used.
Why use Geofabric?
Geofabric, often used interchangeably with geotextile, is favored for its ability to enhance soil stability, promote drainage, and prevent erosion. Its use is critical in construction and environmental projects for its role in providing separation between different soil layers, filtering water, reinforcing embankments, and protecting geomembranes. This separation function is key to maintaining the integrity of various layers, preventing the mixing of materials that could compromise structural stability. The choice to use geofabric is driven by its cost-effectiveness, durability, and the efficiency with which it addresses common geotechnical challenges, including the crucial aspect of layer separation.
Understanding geocomposite prices involves more than just looking at numbers; it requires an appreciation of the material’s composition, types, applications, and benefits over similar products like geotextiles. Geocomposites offer a multifunctional solution that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a wide range of engineering projects. Their cost is reflective of their versatility, advanced functionality, and the value they bring to construction and environmental applications. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of geocomposites and their cost-benefit analysis will undoubtedly remain a topic of interest for professionals seeking innovative and efficient solutions.

Comments
Post a Comment