Safeguarding Our Slopes: The Role of Geocells in Erosion Protection
The battle against slope erosion is an ongoing challenge in geotechnical engineering, a field dedicated to understanding and managing Earth’s physical properties in construction and land use. One innovative solution that has risen to prominence is the use of geocells. These cellular confinement systems offer a sustainable, efficient way to protect slopes from erosion, supporting soil stability and vegetation growth. This popular science article delves into the concept of geocells, exploring their role, application, and unique characteristics in slope erosion protection.
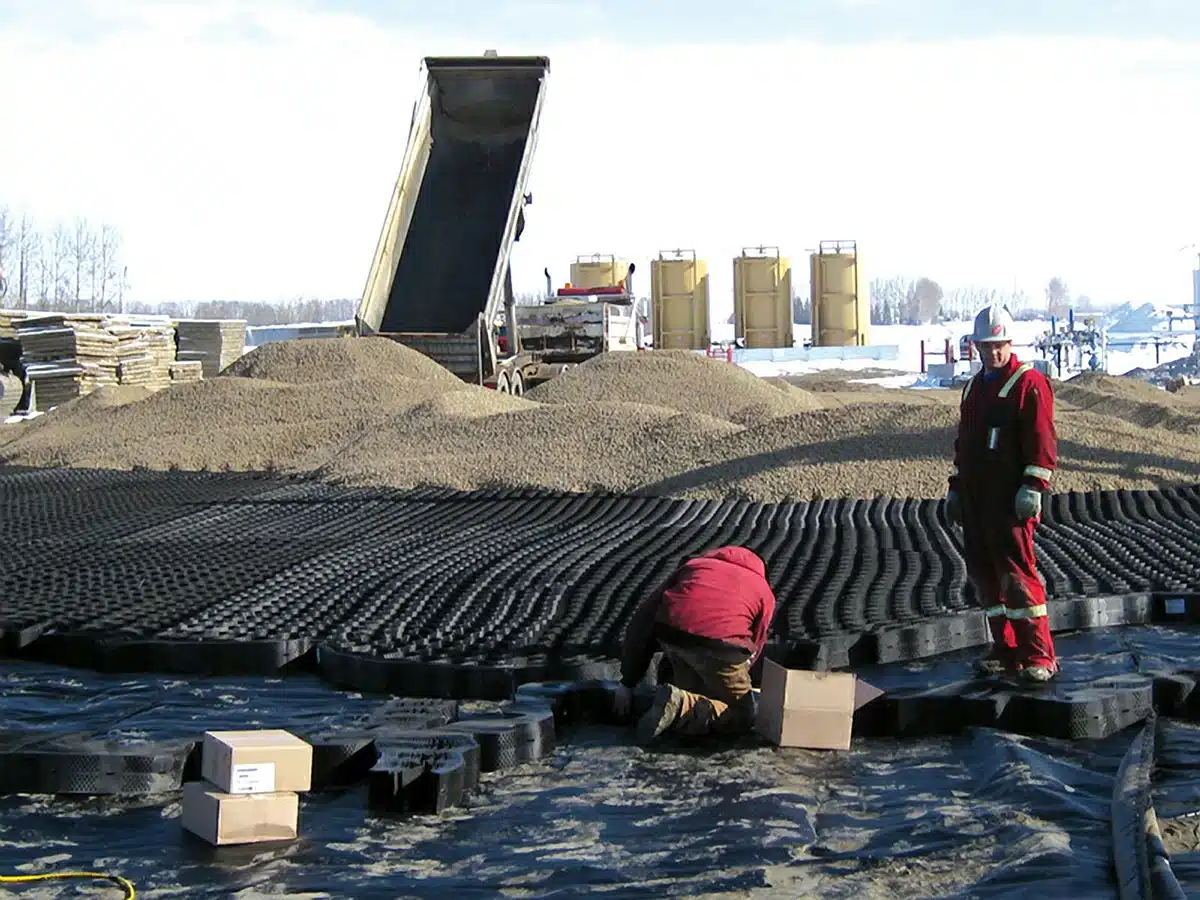

What is a Geocell for Slope Protection?
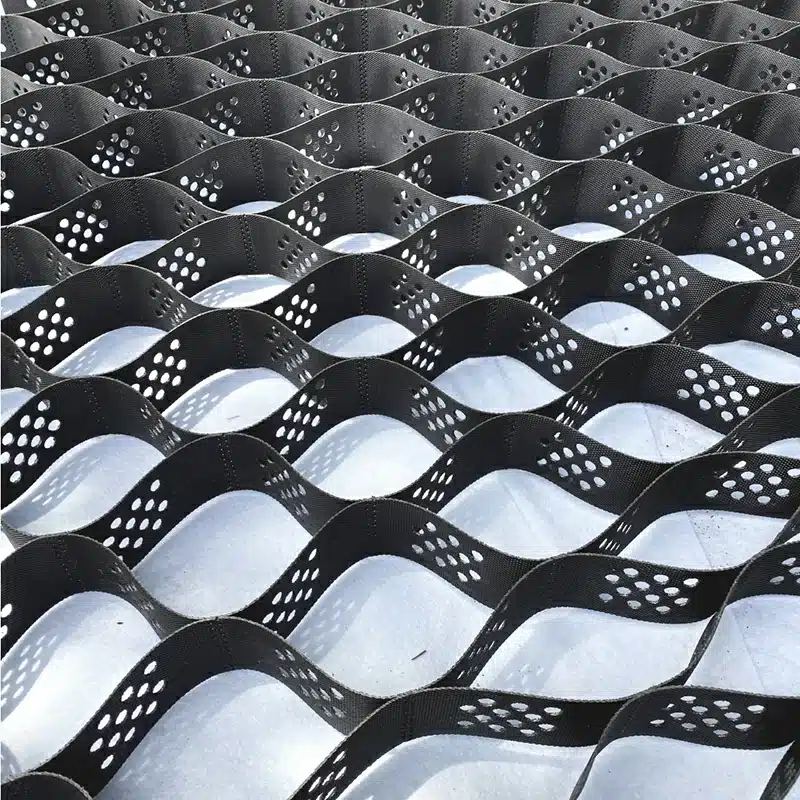
A geocell for slope protection is a three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structure made from durable, lightweight materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), employed to protect slopes from erosion and assist in stabilizing the surface. When expanded and filled with soil, sand, or aggregate, these cells create a stable and flexible framework that enhances load distribution, minimizes soil erosion, and promotes vegetation growth. This effective solution is pivotal for maintaining slope stability. By confining the fill material, geocells not only prevent downward soil movement but also serve as a critical defense against surface erosion, safeguarding embankments, riverbanks, and hillsides from degradation.
What are the Slope Protection Measures in Geotechnical Engineering?
Geotechnical engineering employs various measures to protect slopes from erosion and instability, including mechanical stabilization techniques such as retaining walls and anchors, vegetative solutions like hydroseeding, geotextiles, erosion control blankets, and turf reinforcement mats, as well as innovative technologies among which geocells are prominent. Each method addresses different aspects of slope stability, providing everything from immediate structural support to promoting long-term vegetation development. Erosion control blankets and turf reinforcement mats, similar to geotextiles, offer additional support for vegetation establishment, thereby enhancing slope protection. Geocells, in particular, stand out for their unique combination of flexibility, durability, and environmental friendliness, making them a preferred choice for a wide range of applications.
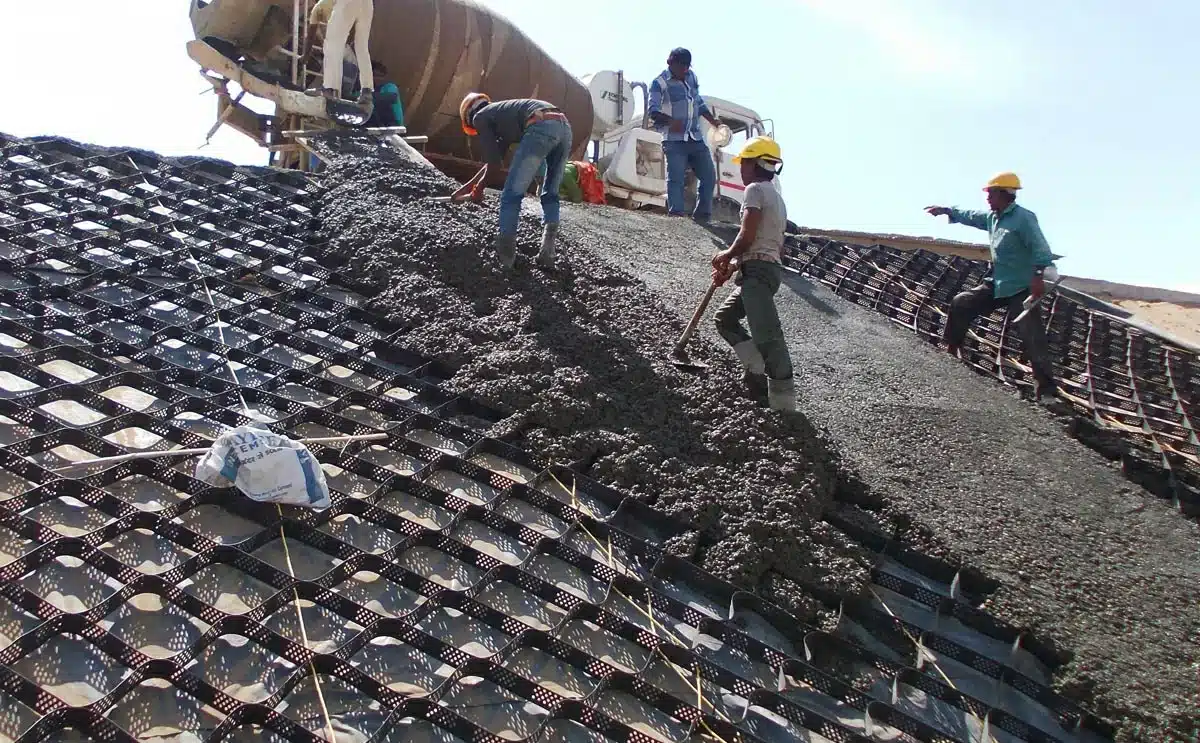

What is a Geocell?
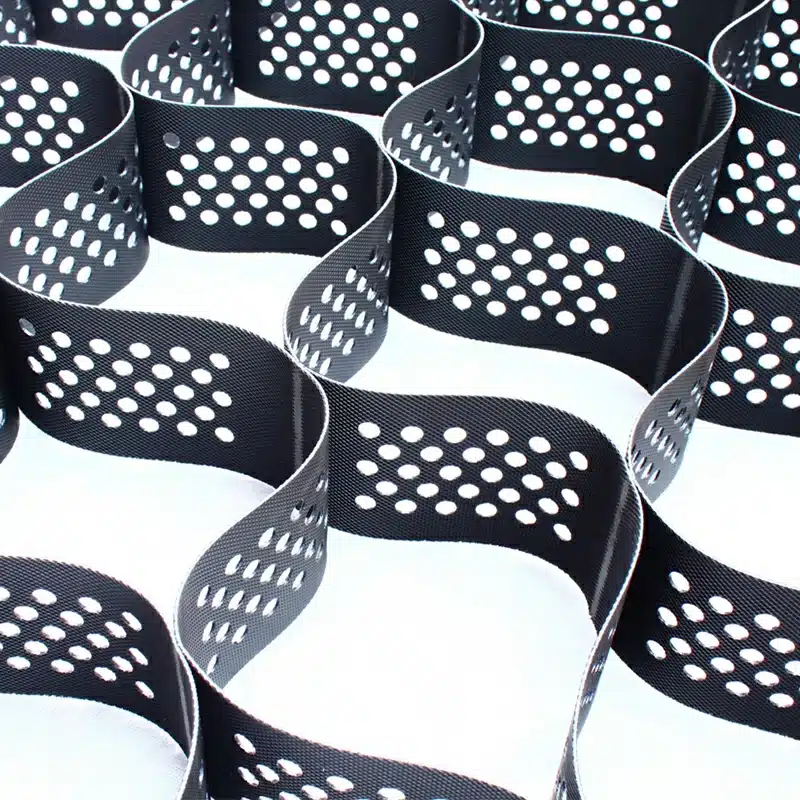
A geocell is a three-dimensional, net-like structure that acts as a highly flexible and permeable confinement system when filled with soil, stone, or concrete. Specifically, it is one of the cellular confinement systems made from strips of welded high-density polyethylene (HDPE) that form a honeycomb grid when expanded and are filled with aggregate or soil. This design allows it to be utilized in various applications, from slope protection and soil stabilization to channel protection and load support. Geocells, constructed from polymers such as HDPE, are celebrated for their environmental resistance, strength, and longevity. Their innovative cellular design enables them to distribute loads evenly, reduce shear forces, and enhance the mechanical properties of the infill material, marking them as an effective stabilization technique in geotechnical engineering.
What are the Characteristics of a Geocell?
Geocells exhibit several defining characteristics that make them suitable for slope erosion protection and other geotechnical applications, highlighting their versatility and efficiency:
- Flexibility and Strength: Geocells, which can be large or small and can be retracted for transportation, effortlessly conform to uneven landscapes while maintaining structural integrity. This adaptability allows them to support heavy loads and withstand environmental stresses, offering reliable performance across various scenarios.
- Permeability: The cellular structure not only allows water to flow through, reducing hydrostatic pressure and promoting drainage but is also crucial for slope stability and vegetation growth. This feature ensures that geocells contribute significantly to the overall health and sustainability of the environment they are installed.
- Durability: Designed to endure, geocells are made from UV-resistant and chemically stable materials. Their durability is a testament to their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring they remain a steadfast solution for years.
- Eco-Friendly: Emphasizing sustainability, geocells are often manufactured from recycled materials. They support vegetation growth, contributing to ecosystem restoration and carbon sequestration, thereby playing a pivotal role in environmental conservation efforts.
Cost-Effective: Geocells offer a cost-efficient solution for large-scale engineering projects thanks to their easy installation and maintenance, coupled with their long-term durability. Their ability to be easily transported, due to their retractable nature, further underscores their practicality and cost-effectiveness in a wide range of applications.
Geocells have emerged as a versatile and effective solution for combating slope erosion, offering a blend of mechanical support, environmental protection, and cost efficiency. Their application in geotechnical engineering not only safeguards infrastructure and landscapes but also promotes sustainable development practices. As we continue to face the challenges of land degradation and environmental change, the role of geocells in slope erosion protection exemplifies the innovative approaches necessary for a stable and resilient future.


Comments
Post a Comment