Strengthening Infrastructure: How GeoNets Enhance Stability
In the ever-evolving world of geotechnical engineering, materials that can solve complex environmental and construction-related challenges are in constant demand. Enter the GeoNet, a term that might sound straight out of a science fiction novel but is very much grounded in the practical needs of today’s engineering feats. A geonet is a geosynthetic material similar in structure to a geogrid, consisting of integrally connected parallel sets of ribs overlying similar sets at various angles for in-plane drainage of liquids or gases. This article delves into the essence of GeoNets, exploring their purpose, applications, composition, and functionality, shedding light on how they contribute to the stability and sustainability of the infrastructure that underpins modern society.
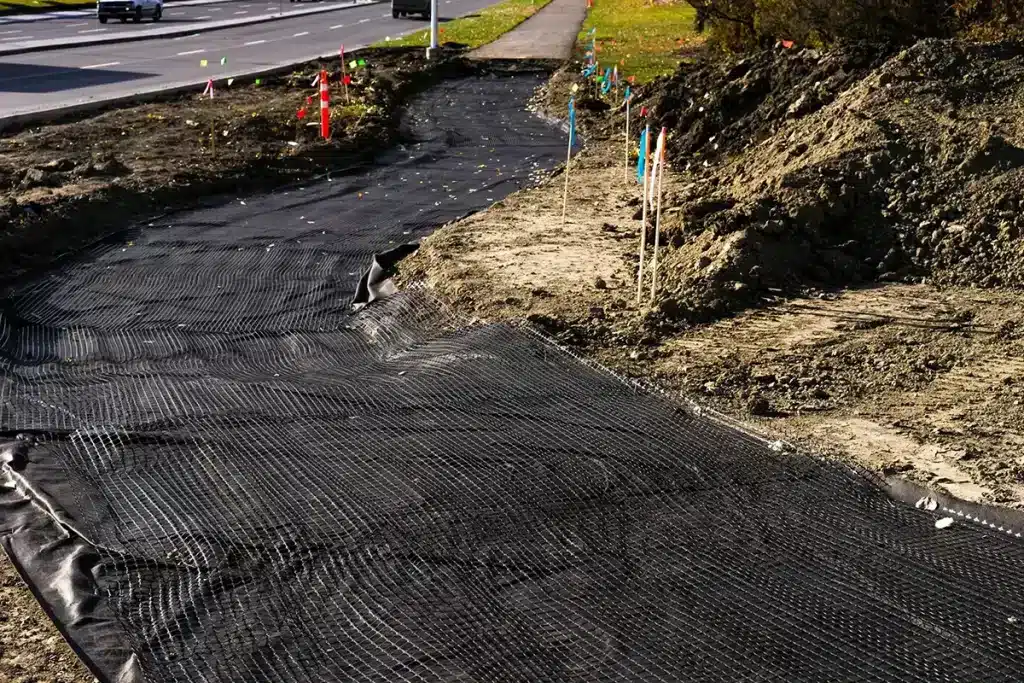

What is the purpose of a GeoNet?
GeoNets serve a pivotal role in environmental and geotechnical engineering, particularly in erosion control. Their primary purpose is to facilitate effective drainage and stabilization in a variety of construction and environmental projects, including those aimed at combating erosion. By providing a pathway for the flow of fluids and gases, GeoNets help manage water and methane in landfills, prevent soil erosion, and maintain the integrity of civil engineering works. Their unique structure allows them to distribute loads evenly, reducing stress on underlying materials and enhancing the lifespan of engineering projects, making them an indispensable tool in erosion control strategies.
What are the applications of GeoNet?
The versatility of GeoNets is showcased through their wide range of applications, encompassing an impressive array of projects including road construction, road widening, asphalt work, building construction and foundations, retaining walls, dams, artificial ponds, and water reservoirs, among many others. They are extensively used in landfill liners and covers, providing crucial drainage layers that prevent water accumulation and gas build-up. In the realm of road infrastructure, GeoNets act as sub-base layers, improving stability and drainage, thereby prolonging the road’s life. This includes not just new road construction but also the widening of existing roads and the laying of asphalt. In the construction sector, GeoNets are pivotal in the foundations of buildings, enhancing their stability and durability. Furthermore, their role extends to erosion control projects to protect vulnerable slopes and embankments, as well as in the construction of retaining walls, where they assist in managing water pressure and reinforcing the soil. GeoNets are also employed in the creation of dams, artificial ponds, and water reservoirs, showcasing their critical importance in managing water resources and infrastructure.
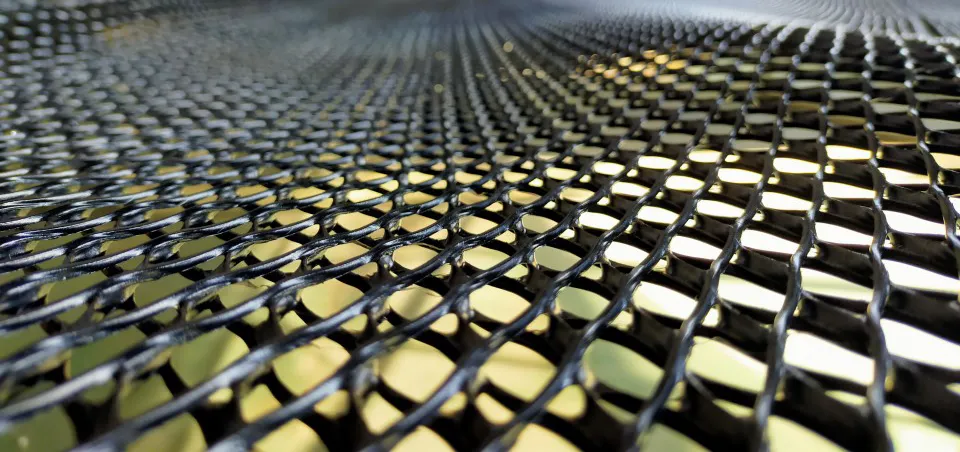
What is a GeoNet made of?
GeoNets are typically made from virgin high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene. These materials, especially virgin HDPE, are chosen for their superior durability, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand physical and environmental stress. The manufacturing process involves extruding the plastic into a net-like structure with interconnected ribs. This design not only provides strength and flexibility but also ensures the material’s permeability, making it ideal for drainage and reinforcement applications. The use of virgin HDPE in particular enhances the long-term performance and reliability of GeoNets, ensuring that they meet the stringent requirements of various engineering applications.
How does a geogrid work?
While GeoNets are focused on drainage and reinforcement, geogrids, a related but distinct material, specialize in soil stabilization and reinforcement. Geogrids work by interlocking with soil, aggregates, or other materials, creating a composite that distributes loads over a wider area. This interaction not only improves the overall stability of the soil, preventing shear failure and settlement but is also used to create a reinforced coherent mass behind the retaining wall by stabilizing the soil. Such applications significantly enhance the structural integrity and longevity of various projects. Geogrids are commonly used in road construction, embankments, and retaining walls, where they serve this critical function, ensuring that these structures can withstand the pressures and challenges they face over time.
GeoNets represent a critical innovation in the field of geotechnical engineering, offering solutions to some of the most challenging problems faced by construction and environmental projects. From enhancing drainage to reinforcing and stabilizing soil, their applications are as diverse as they are vital. Understanding the purpose, applications, and workings of GeoNets and related materials like geogrids, sheds light on the remarkable ways in which engineering continues to improve the resilience and sustainability of our infrastructure, ensuring that it meets the needs of both today and tomorrow.

Comments
Post a Comment