How Geocomposites Reinvent Soil Reinforcement & Drainage Solutions
In the vast and ever-evolving field of civil engineering, materials technology stands as a testament to human ingenuity. Among these innovations, geocomposites have emerged as a cornerstone in modern construction and environmental projects. Combining the strength and versatility of geosynthetics, geocomposites offer solutions to a myriad of engineering challenges. This article delves into the essence of geocomposites, exploring their applications, benefits, and types, shedding light on why they have become indispensable in today’s construction and environmental conservation efforts.
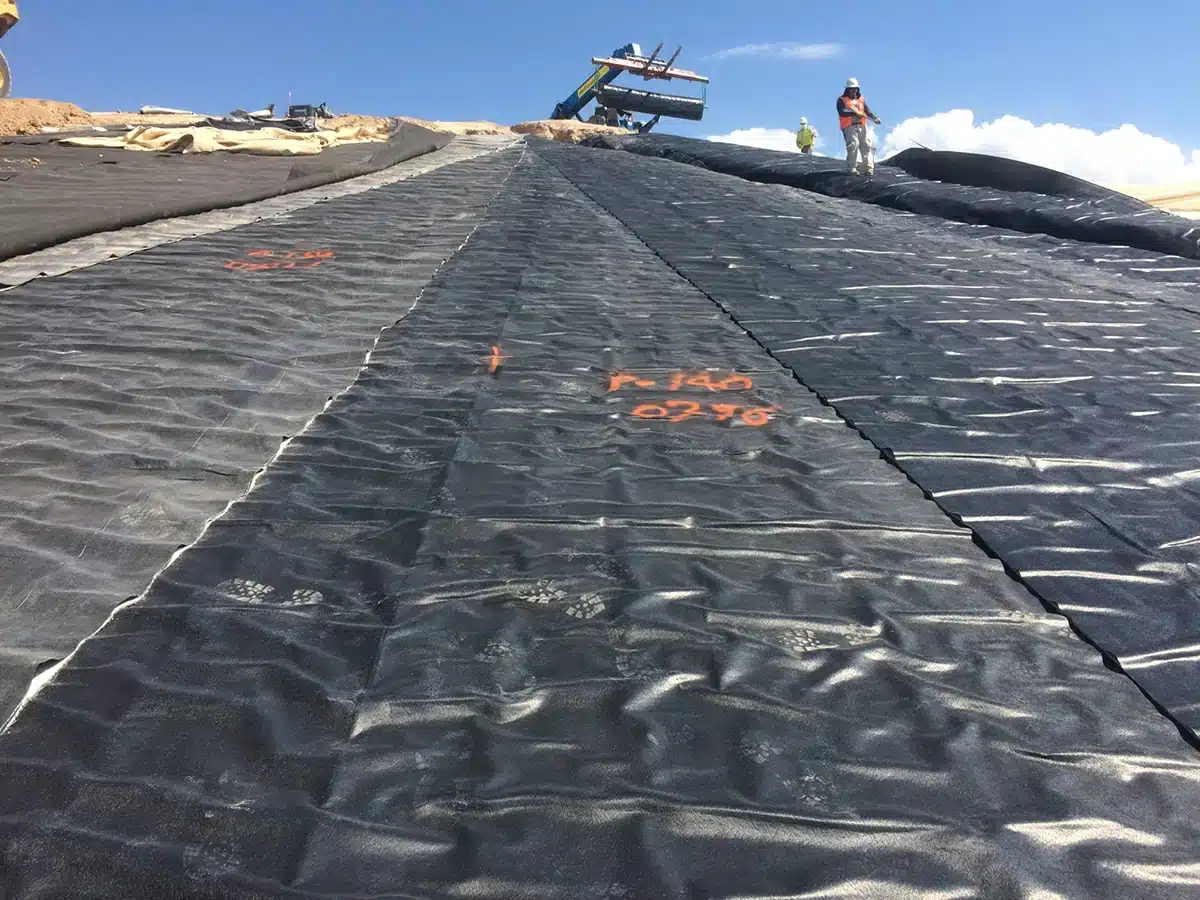

What is a Geocomposite Used For?
Geocomposites are multifaceted materials used to address various engineering and environmental problems. Primarily, they serve to reinforce soil, manage water flow, and act as barriers against erosion or contaminants. Their application is crucial in the construction of roads, railways, landfills, and drainage systems, where they enhance durability and sustainability. Specifically, they are instrumental for drainage from a basal layer in the case of embankments and for drainage behind retaining walls and/or bridge abutments, showcasing their critical role in water management and infrastructure protection. By merging different materials, geocomposites exploit the strengths of each, offering a tailored solution that is both efficient and cost-effective. Their versatility further extends to providing protection for waterproof membranes, thus ensuring the longevity of infrastructure projects.
What is a Geocomposite Drainage Layer?
A geocomposite drainage layer is a specialized configuration designed for effective water management within civil engineering structures. This layer typically combines a geotextile filter and a drainage core, which can collect and convey both liquids and gases, facilitating the swift removal of water while preventing the passage of soil particles. Ideal for applications requiring high-capacity drainage, such as behind retaining walls, under roads, or around buildings, these layers play a pivotal role in preventing water accumulation and the consequent structural damage. Their ability to handle various forms of moisture and air significantly enhances their utility in a wide range of situations. Additionally, their lightweight nature and ease of installation make them a preferred choice over traditional drainage solutions like gravel layers.
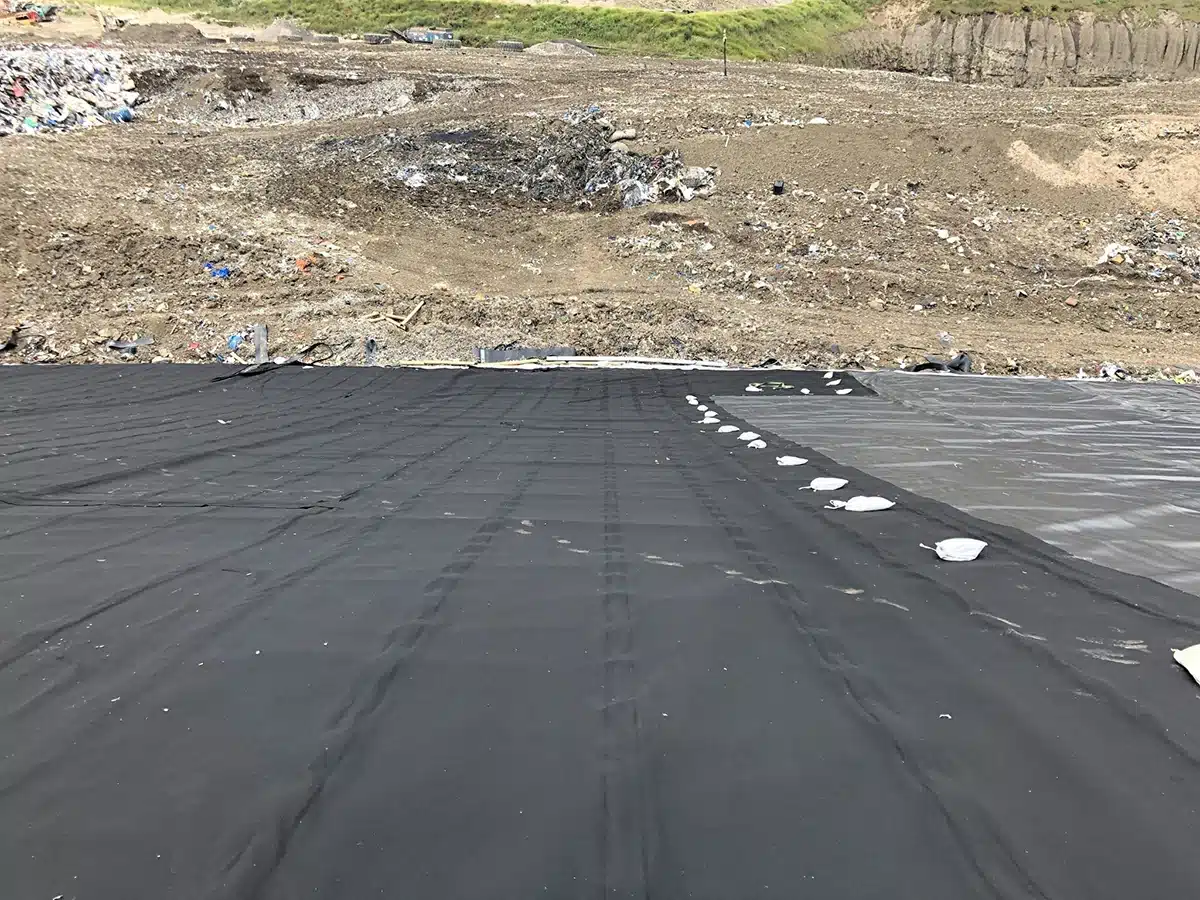

Where are Geocomposites Used?
The versatility of geocomposites allows their application across a wide range of sectors. Civil engineering, they are instrumental in constructing roads, railways, and airport runways, addressing the primary functions of roadways such as separation, drainage, filtration, and reinforcement, where ground stabilization and water management are paramount. Environmental projects benefit from geocomposites in the form of erosion control and landfill liners, safeguarding natural resources and human health. Moreover, their use in agricultural and aquaculture projects for soil reinforcement and water purification showcases their adaptability to various environmental conditions and project requirements, further highlighting their essential role in supporting the foundational aspects of infrastructure development and environmental conservation.
What are the Different Types of Geocomposites?
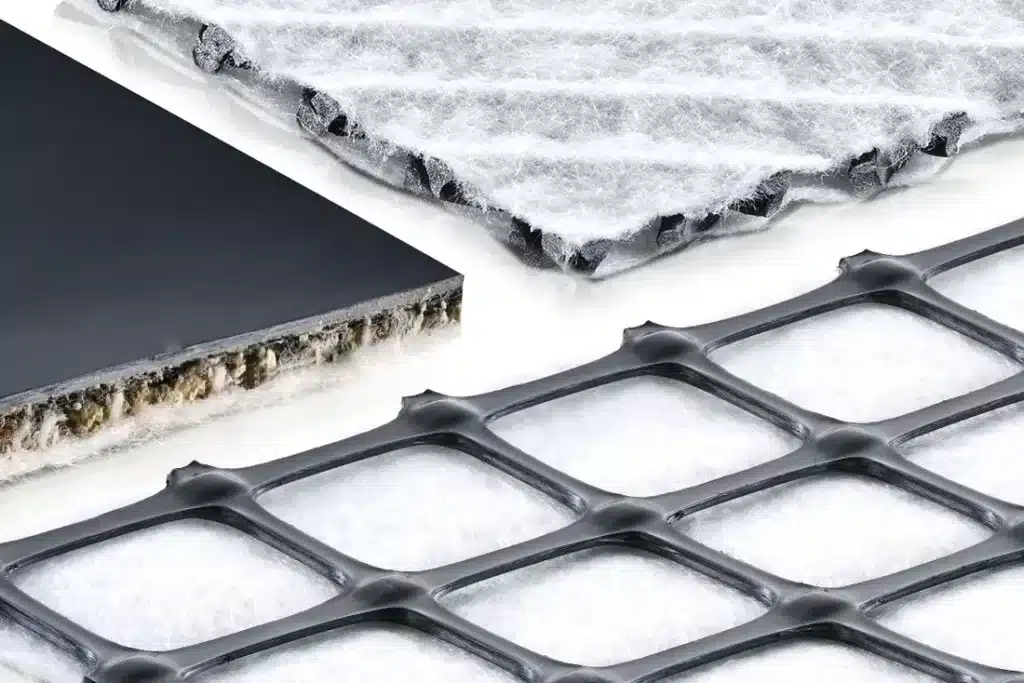
Geocomposites come in several types, each tailored to specific needs and applications. The primary categories now include drainage geocomposites, reinforcement geocomposites, and fluid barrier geocomposites, further categorized as follows:
- Geonet composites: Falling under drainage geocomposites, these are designed for efficient water conveyance, consisting of a drainage core with geotextiles on either side to filter soil and other particles.
- Geomembrane composites: A type of fluid barrier geocomposites, used as barriers to prevent fluid or gas migration in landfills and for contamination control.
- Geogrid composites: Classified as reinforcement geocomposites, these feature a grid-like structure to stabilize slopes and foundations, aimed at soil reinforcement.
- Geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs): Another form of fluid barrier geocomposites, combining a layer of bentonite clay between fabrics or geomembranes, used for sealing and environmental protection.
Each type represents a solution to specific engineering challenges, from water management to soil stabilization and contamination control, underscoring the diversity and adaptability of geocomposites to various environmental and construction needs.
Geocomposites are a testament to the innovative spirit of materials technology in civil engineering. By offering versatile, efficient, and sustainable solutions, they address a wide array of challenges in construction, environmental projects, and beyond. Understanding the types, applications, and benefits of geocomposites not only highlights their importance in modern engineering but also underscores the continual need for advancement in construction materials. As we move towards a future where sustainability and efficiency are paramount, geocomposites stand as a beacon of innovation, paving the way for smarter, more resilient infrastructure.


Comments
Post a Comment