How Geocell Retaining Walls Reinforce and Stabilize Slopes
Retaining walls is crucial in engineering to prevent soil erosion, manage slopes, and support terrains. Among the various types of retaining walls, geocell retaining wall systems have emerged as a significant innovation. This article explores the concept of geocell retaining walls, their design principles, advantages, and typical applications. By integrating lightweight and flexible materials into complex geological settings, geocell retaining walls provide sustainable and cost-effective solutions for various engineering challenges.
What is a Geocell Retaining Wall?
A geocell retaining wall is a type of earth retention system that uses three-dimensional honeycomb-like structures made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) to stabilize and contain soil. The geocells are expanded on-site and filled with local soil, aggregate, or concrete, forming a flexible, permeable, and strong wall. This structure effectively holds the earth in place and distributes loads evenly, which is essential in steep or unstable terrains.
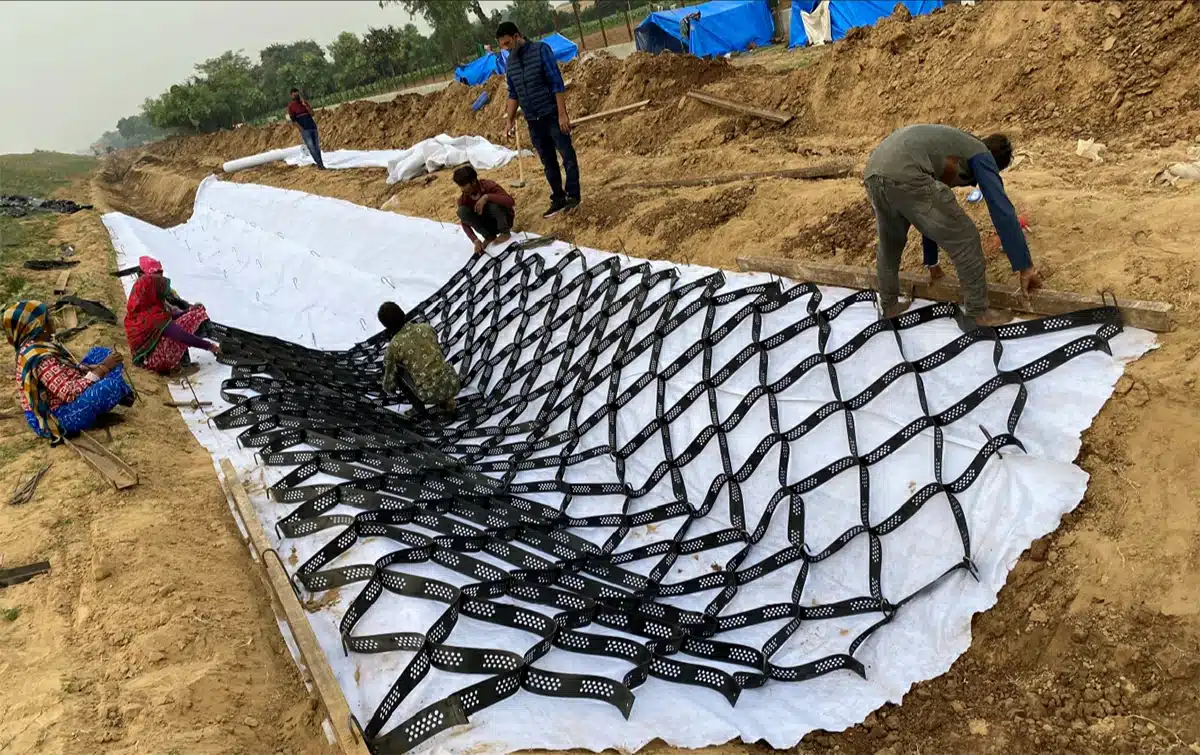

How are Geocell Retaining Walls Designed?
Designing a geocell retaining wall involves several key steps:
- Site Assessment: Evaluating soil characteristics, slope conditions, and load requirements.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate geocell material that can withstand environmental and mechanical stresses.
- Geocell Layout: Determining the layout, height, and depth of the geocell layers to ensure stability.
- Filling Material: Selecting the right type of fill material, which can be soil, sand, or gravel, depending on the specific requirements of the site.
- Drainage Considerations: Integrating efficient drainage solutions to prevent water accumulation and pressure buildup behind the wall.
- Construction Techniques: Implementing proper installation methods to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the retaining wall.
What are the Advantages of Using Geocell Retaining Walls?
Geocell retaining walls offer several advantages over traditional retaining wall systems:
- Versatility: They can be used in a variety of soil conditions and terrains.
- Durability: HDPE materials are resistant to chemical degradation, weathering, and physical wear.
- Cost-effectiveness: Using local materials for fill reduces transportation costs and overall project expenses.
- Environmentally Friendly: Geocells are often made from recycled materials and facilitate vegetation growth, which can integrate seamlessly into natural landscapes.
- Ease of Installation: Lightweight and easy to transport, geocell systems can be quickly installed, reducing labor costs and time.
What Are Typical Applications of Geocell Retaining Walls?
Geocell retaining walls are versatile and can be applied in numerous scenarios, including:
- Highways and Railroads: For stabilizing embankments and slopes adjacent to roadways.
- Landscaping: In residential and commercial properties for aesthetic and functional terrain shaping.
- Erosion Control: On riverbanks and coastal areas to prevent soil erosion.
- Mining: As part of heap leach pads and tailings dams in the mining industry.
- Agriculture: For terracing agricultural fields to improve usability and reduce erosion.
Geocell retaining walls represent a significant advancement in civil engineering, offering a flexible, durable, and cost-effective solution for soil stabilization and erosion control. Their design allows for adaptation to varied terrains and conditions, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. By understanding and implementing geocell technology, engineers can effectively tackle challenging geological issues, promoting safety and sustainability in infrastructure development.


Comments
Post a Comment