Revolutionizing Landscape Engineering: The Role of GeoCell in Cover-Retaining Wall Systems
In the realm of civil engineering and landscape architecture, retaining walls play a critical role in managing soil erosion, supporting structures, and maintaining the aesthetic appeal of sloped terrains. Among the various technologies employed, GeoCell systems have emerged as a groundbreaking solution. This article delves into the specifics of GeoCell technology, exploring its applications, benefits, and mechanisms in covering retaining wall systems.
What is a GeoCell Retaining Wall?
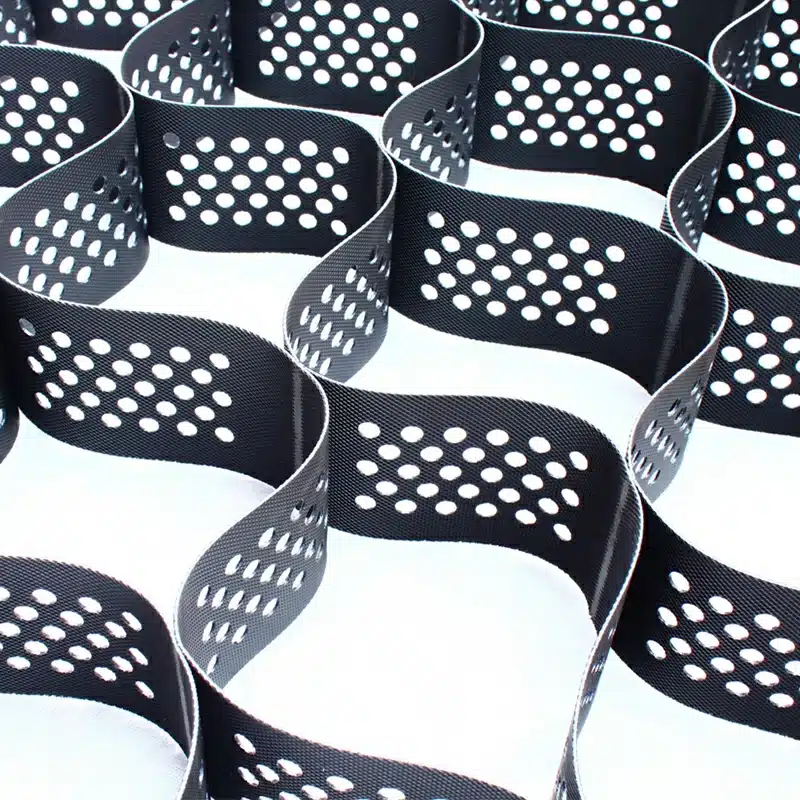
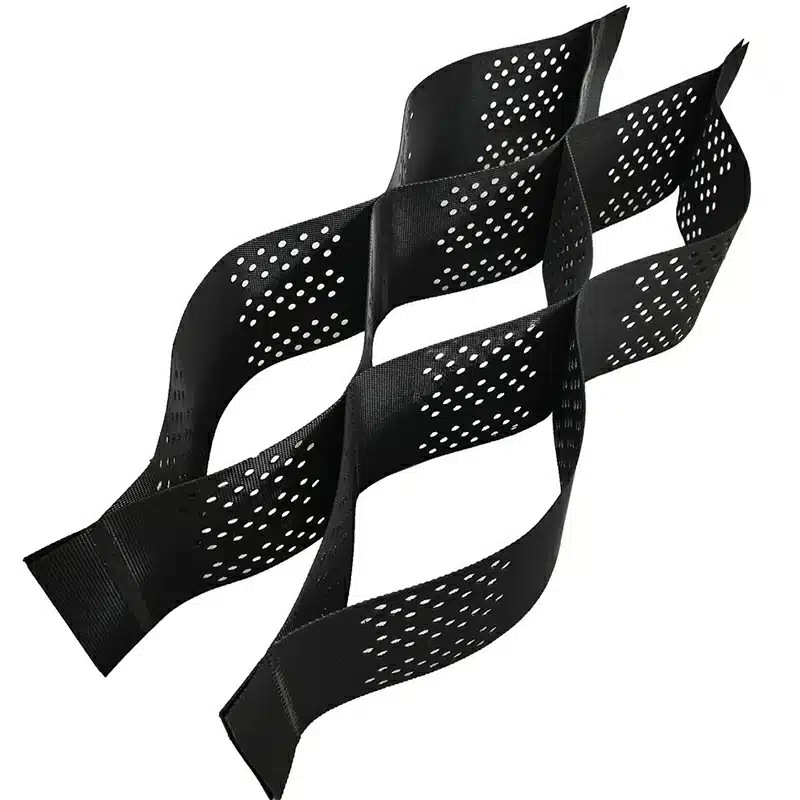
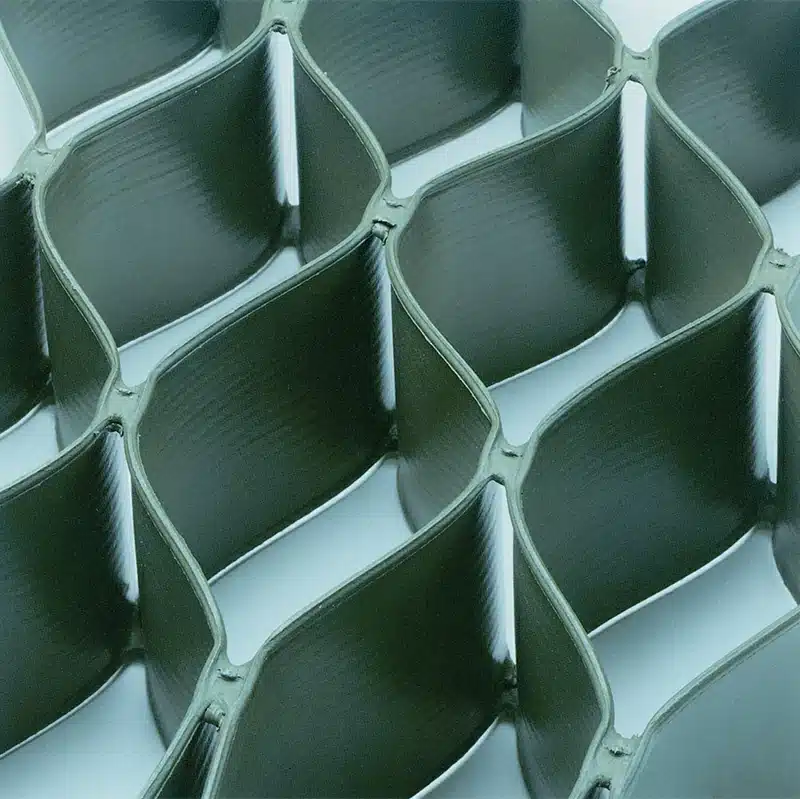
A GeoCell retaining wall is a type of cellular confinement system that features a three-dimensional cellular structure, typically crafted from high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This honeycomb-like grid is expanded on-site and can be filled with soil, gravel, or other materials. Such filling within the interconnected cells helps to confine the materials effectively, providing stability and strength to the retaining wall. GeoCell walls are particularly valuable not only for retaining soil but also for enhancing load distribution, which is crucial in preventing wall failures and ensuring longevity.
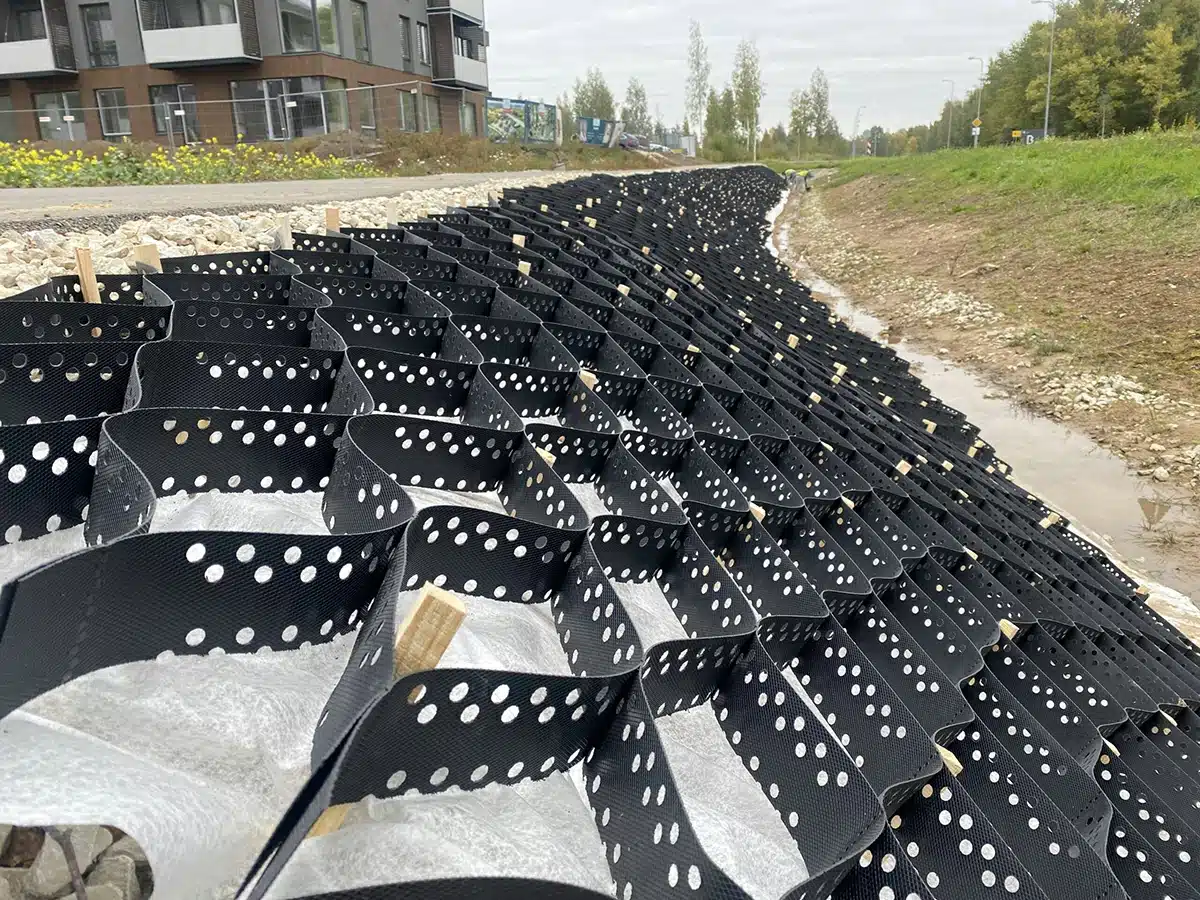

What is the purpose of GeoCell?
The primary purpose of GeoCell is to provide a flexible, durable, and environmentally friendly solution to soil stabilization challenges. GeoCells are adept at addressing multiple needs including erosion control, soil stabilization on flat ground and steep slopes, channel protection, and structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention. They are designed to adapt to varying landscapes and can be used in a range of applications from road construction to managing water drainage effectively. In retaining walls, GeoCells enhance structural stability and prevent soil erosion. Their versatility and efficiency make them an excellent choice for both temporary and permanent structures in challenging terrains.
What is GeoCell in slope protection?
In slope protection, GeoCells act as armor that shields the slope from erosion caused by water runoff, wind, and other natural elements. Employed to protect slopes from erosion and assist in stabilizing the surface, the cellular confinement system prevents the downward movement of soil particles, thereby maintaining the integrity of the slope. By improving the load-bearing capacity of the slope surface, GeoCells reduce the risk of landslides and other soil movement issues, making them an integral part of slope stabilization strategies.
What is the mechanism of GeoCell?
The mechanism of GeoCell revolves around the principle of cellular confinement. When expanded and anchored to the ground, the GeoCell grid traps and holds soil or other materials within its cells. This confinement effect from the geocell walls creates a stiff layer that distributes loads evenly across a wider area. Moreover, the flexural capacity and tension membrane action of the geocell layer contribute to its effectiveness. The three-dimensional structure of the GeoCell also allows for thermal expansion and contraction, which is essential in varying climatic conditions. Additionally, the perforations in the cell walls facilitate water drainage, thus maintaining soil hydration levels without causing waterlogging or erosion.
GeoCell technology offers an innovative and efficient approach to constructing retaining walls and protecting slopes. Its unique cellular design not only ensures structural stability but also promotes environmental sustainability through effective erosion control. Whether in urban construction or rural landscaping, GeoCell systems provide a reliable and adaptable solution that meets the dynamic demands of modern engineering challenges. By integrating GeoCell into their projects, engineers, and architects can achieve enhanced performance and durability, safeguarding structures against the elements and time.


Comments
Post a Comment