Enhancing Stability with Sand Finish Geomembranes: Where and Why to Use Them
Geomembranes are an integral component in modern engineering, offering versatile solutions to problems in environmental, hydraulic, and geotechnical applications. Among the various types of geomembranes, sand-finish geomembranes stand out due to their unique texture and enhanced performance in certain applications. This article delves into the specifics of sand finish geomembranes, exploring their uses, types, installation methods, and ideal application scenarios.
What is a geomembrane used for?
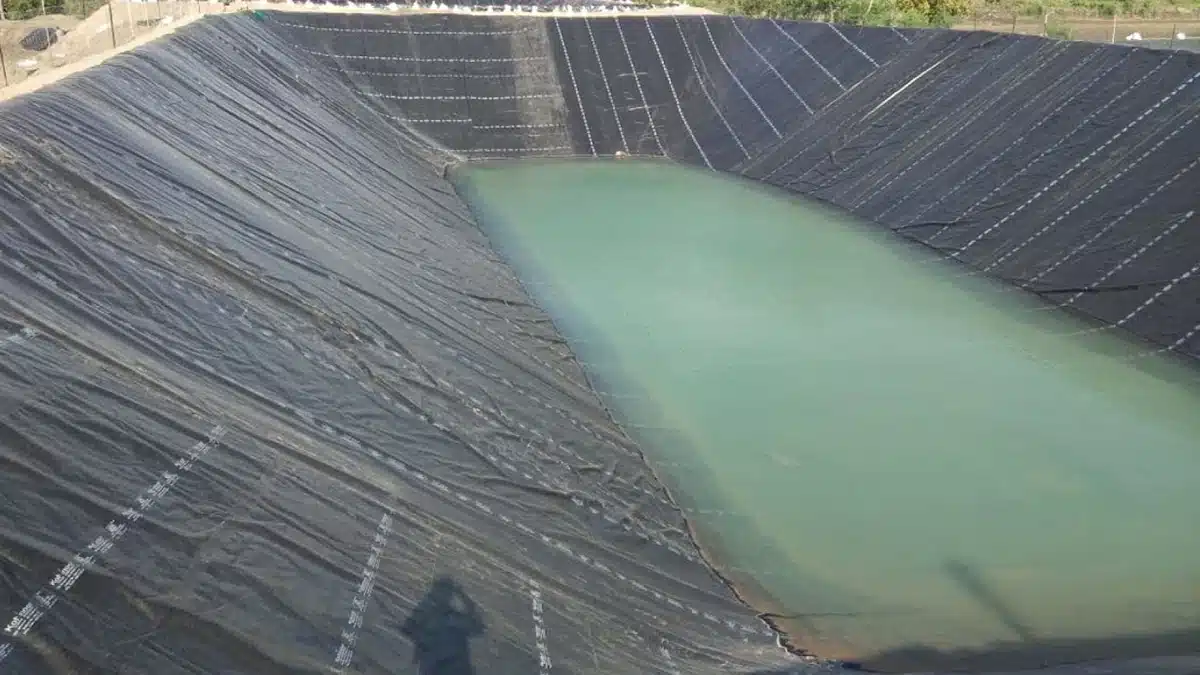
Geomembranes serve a crucial role in containing and managing liquids, gases, or solids to prevent contamination of the environment. They are widely used in various sectors, including waste containment, such as landfill liners designed to stabilize earth and secure landfills, ensuring containment of hazardous or municipal wastes and their leachates. They are also used in water reservoirs, floating covers for odor control, and aquaculture. Sand finish geomembranes, with their rough surface, are particularly effective in preventing slippage in steep slopes and enhancing the stability of covered materials.

What are the three types of geomembranes?
Geomembranes are typically classified into three main types based on their material composition: PVC-P (Polyvinyl Chloride Plasticized), HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), and EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer):
- HDPE Geomembranes: Known for their high chemical resistance and strength, making them suitable for applications in waste containment and chemical processing facilities.
- PVC-P Geomembranes: These are flexible and adaptable to various shapes, ideal for water ponds and irrigation systems. PVC-P offers enhanced flexibility compared to traditional PVC.
- EPDM Geomembranes: EPDM is highly durable and weather-resistant, often used in decorative ponds and various water containment scenarios.
When to use a geomembrane?
The decision to use a geomembrane depends on the need for a highly effective barrier against contaminants and environmental conditions, particularly as barriers to moisture and gas flow. For instance, in projects where there is a high risk of soil or water contamination, such as in landfills or chemical storage facilities, a geomembrane is essential. Sand finish geomembranes are specifically chosen when there is a need for increased frictional performance, such as in slopes and embankments, to ensure stability and safety. These geomembranes not only prevent contaminants from escaping or entering but also effectively block moisture and gases, further protecting the environment.
How are geomembranes installed?
The installation of geomembranes is a meticulous process that requires professional handling:
- Site Preparation: The area must be cleared of any objects that might puncture the geomembrane. The base is usually prepared with a smooth layer of sand or clay.
- Deployment: Rolls of geomembrane are laid out and positioned correctly over the prepared base. This stage involves the careful positioning and unfolding of the rolls or panels, particularly crucial for sand finish geomembranes where the orientation of the textured surface must be carefully managed.
- Seaming: The edges of adjacent geomembrane sheets are welded or bonded together to form a continuous barrier. This can be done using thermal fusion, solvent welding, or adhesive bonding, depending on the material type.
- Testing: Once installed, the seams and the geomembrane itself are tested for integrity to ensure there are no leaks or weaknesses.
Sand finish geomembranes represent a crucial development in the field of synthetic barriers, providing effective solutions to environmental challenges. Whether it’s managing waste, securing water resources, or ensuring the safety of civil engineering structures, these geomembranes play a pivotal role in safeguarding our natural and built environments. With their unique sand finish, they offer added stability and efficiency, making them a preferred choice for challenging applications. Understanding when and how to use these materials is key to leveraging their benefits in various industrial and environmental contexts.


Comments
Post a Comment