Essential Uses of Geogrids for Soil Reinforcement and Erosion Control
Geogrids are a revolutionary technology in the field of civil engineering, offering enhanced stability and support in various construction and landscaping projects. These grid-like synthetic materials are crucial for reinforcing soil, improving load capacity, and preventing erosion. This article explores the pivotal scenarios where geogrids play an essential role, specifically focusing on their applications in retaining walls and other structural needs.
When should you use Geogrid on a retaining wall?
Geogrids are a revolutionary technology in the field of civil engineering, offering enhanced stability and support in various construction and landscaping projects, especially whenever you want your hardscape to last and stay structurally sound. These grid-like synthetic materials are crucial for reinforcing soil, improving load capacity, and preventing erosion. This article explores the pivotal scenarios where geogrids play an essential role, specifically focusing on their applications in retaining walls and other structural needs.
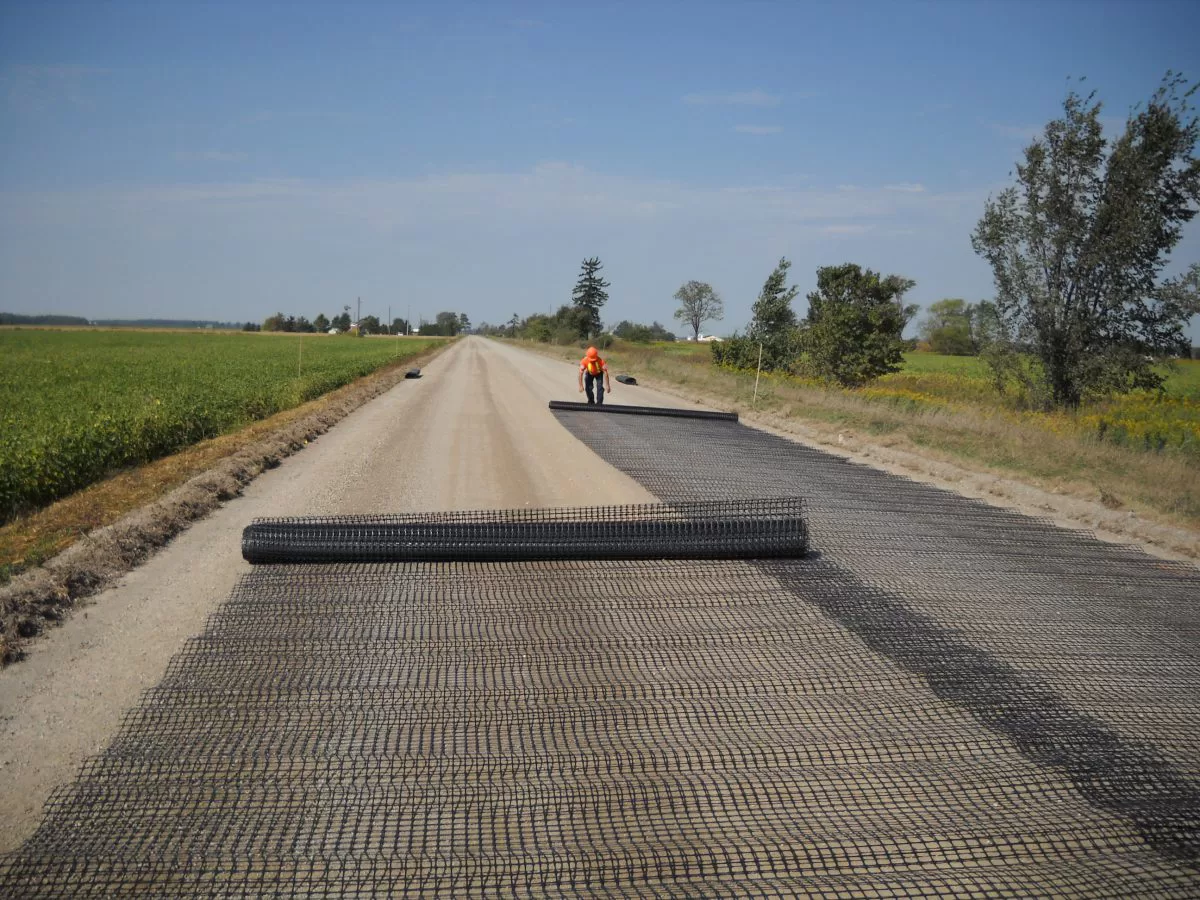

What is Geogrid used for?
Geogrids serve a variety of purposes across civil engineering disciplines, primarily focusing on soil stabilization and reinforcement. This includes applications in road construction, where they enhance pavement life by stabilizing the subgrade layer; in slope protection, to prevent landslides and erosion; and in the construction of embankments over soft soils, where they increase load-bearing capacity. Additionally, geogrids are used in the reinforcement of retaining walls, particularly effective for walls taller than three to four feet, as previously discussed.
At what height do you need a geogrid?
The requirement for geogrids in retaining wall projects generally starts when the wall height reaches about 3 feet (about 0.9 meters) or greater. This threshold can vary based on the type of soil, the slope of the ground, and the load expected on or near the wall. Consulting with a geotechnical engineer is advisable to assess specific needs based on these factors.
What is the spacing between geogrids?
The spacing between layers of geogrids in a retaining wall or other structures depends on the soil type, wall height, and expected loads. Typically, the spacing ranges from 0.3 to 0.8 meters. Accurate spacing is crucial for ensuring that the geogrid layers effectively share the load and enhance the stability of the soil or structure they are reinforcing. Again, specific projects should be evaluated by a professional to determine the optimal spacing for geogrid layers.
Geogrids are an essential tool in modern construction, offering significant benefits for soil stabilization and structural support. Their use in retaining walls is particularly noteworthy, providing necessary reinforcement that enhances safety and durability. Whether you are planning a small garden wall or a major highway embankment, understanding when and how to effectively utilize geogrids can lead to more successful and sustainable construction projects. By consulting with professionals and adhering to recommended practices for geogrid use, engineers and contractors can ensure that their structures stand the test of time.


Comments
Post a Comment