How Biaxial Geogrids Strengthen and Stabilize Soils Effectively
In the realm of civil engineering and construction, stabilizing materials is crucial for enhancing the structural integrity of soils. Among these materials, biaxial geogrid stands out as a particularly effective solution for ground stabilization and reinforcement. This article delves into the nature of biaxial geogrids, exploring their composition, functionality, benefits, and differences from similar materials like geotextiles.

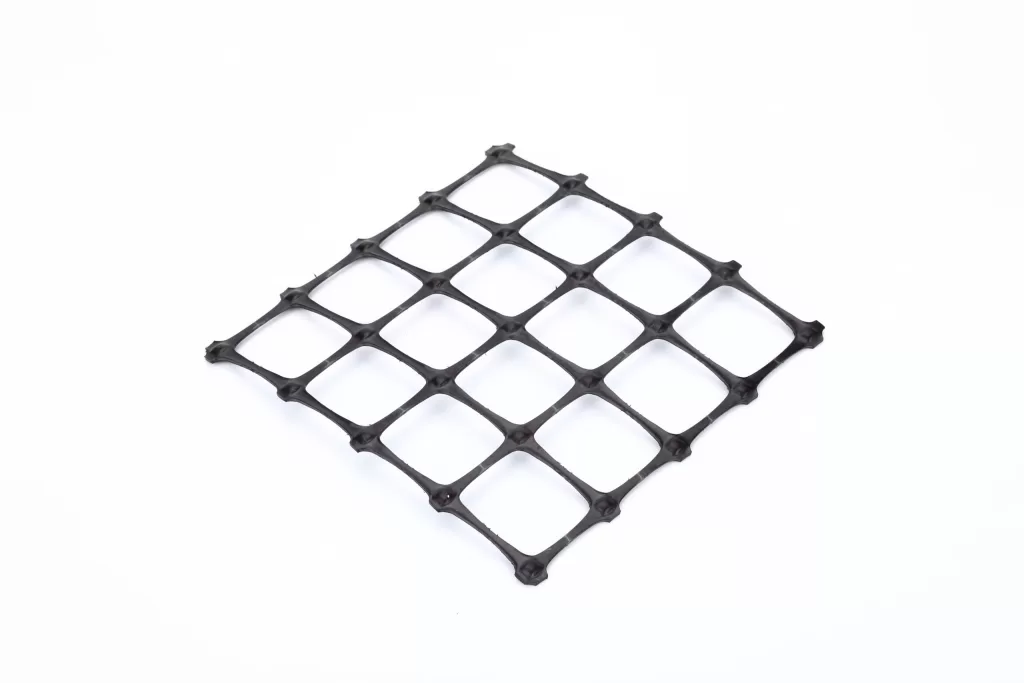
What are the materials in biaxial geogrid?
You are a content editor. Please naturally integrate “Polypropylene” into the following paragraphs. The logic and semantics are smooth and the main idea of the paragraph remains unchanged:
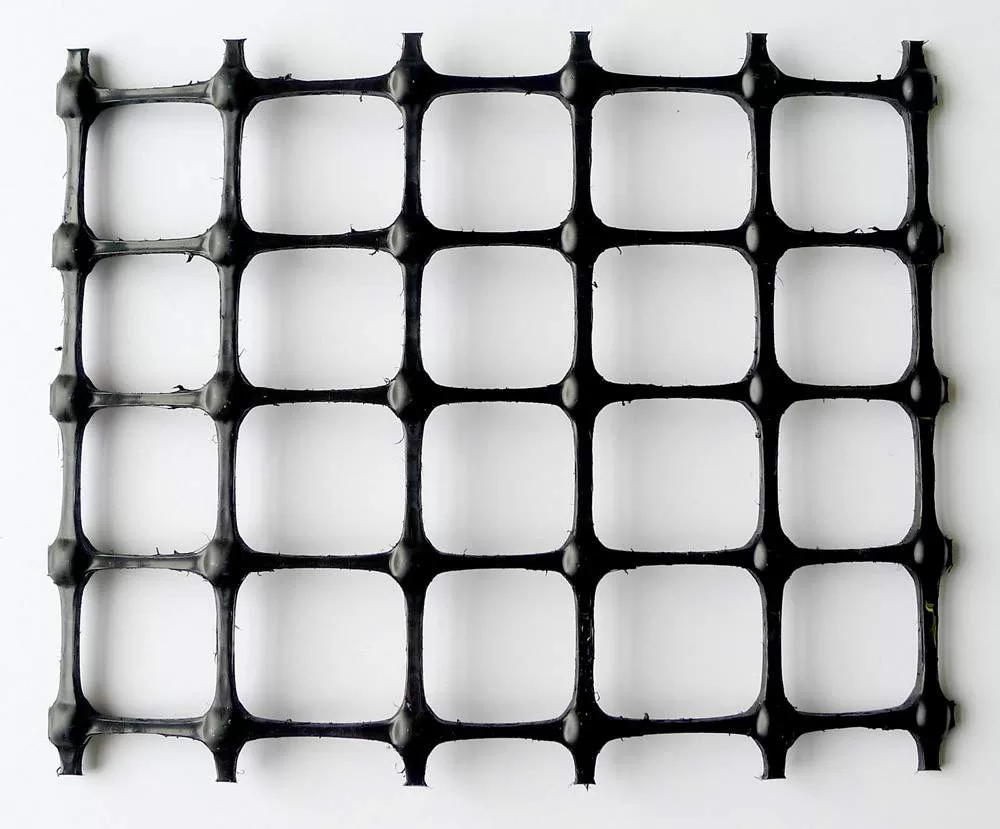
Biaxial geogrids are typically made from polymers such as polypropylene or polyester. These materials are chosen for their high tensile strength and durability. During the manufacturing process, sheets of these polymers are extruded and then punched to create a grid pattern. The resulting structure is stretched in two orthogonal directions (biaxial), which enhances its strength and load distribution capabilities. This makes biaxial geogrids highly effective as stabilizing materials in various civil engineering applications.
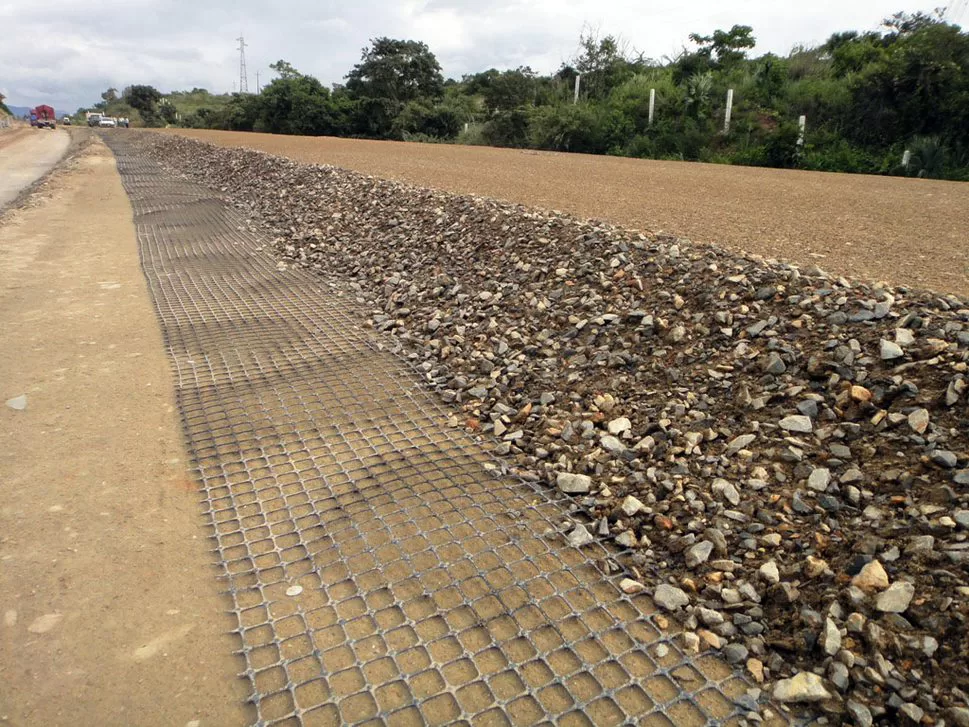
What is geogrid stabilization?
Geogrid stabilization refers to the use of geogrids, which are used in a variety of construction applications for soil stabilization, reinforcement, and erosion control, to improve the load-bearing capacity of soils. When biaxial geogrids are incorporated into the soil, they interlock with the soil particles and distribute loads over a wider area. This process significantly reduces soil settlement and enhances stability. Geogrid stabilization is commonly employed in the construction of roadways, embankments, and retaining walls, where maintaining soil stability is crucial.
What are the benefits of biaxial geogrid?
- Enhanced Load Distribution: It spreads the loads over a broader area, thereby reducing pressure on underlying soils.
- Improved Soil Stability: By reinforcing the soil, it helps prevent soil movement and reduces the risk of erosion.
- Cost Efficiency: Biaxial geogrids can reduce the need for traditional, more expensive construction materials like concrete and large quantities of compacted fill.
- Environmental Benefits: Using geogrids can minimize the environmental impact by reducing the quantity of natural resources required and the overall carbon footprint of construction projects.
- Ease of Installation: Biaxial geogrids are lightweight and easy to install, which can significantly decrease the time and labor costs associated with construction projects.
What is the difference between geogrid and geotextile?
While both geogrids and geotextiles are used for soil stabilization and reinforcement, they differ significantly in their manufacturing purposes and functions. Geotextiles are manufactured for separation, filtration, and drainage purposes, characterized by their permeable fabrics that help prevent the intermixing of different soil layers while allowing water to pass through, which is crucial for drainage and erosion control. In contrast, geogrids are manufactured specifically as a reinforcement material and are characterized by their open grid-like structure, which allows them to interlock with soil particles and provide tensile reinforcement. This makes geogrids more suited for structural support and load distribution.
Biaxial geogrid represents a robust and versatile stabilizing material in the field of civil engineering, offering substantial benefits in terms of soil stabilization, cost efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Its unique material composition and structural characteristics make it an ideal choice for reinforcing challenging soil conditions and extending the lifespan of infrastructure projects. Understanding the distinct functions and advantages of geogrids over other materials like geotextiles can help in choosing the right solution for specific engineering challenges.


Comments
Post a Comment