What Are Geomembranes? Key Types and Uses in Engineering
Prefabricated geomembranes are synthetic membranes widely used in various applications, including landfill lining, wastewater treatment, and aquaculture. Engineered for durability and impermeability, these materials provide effective barriers against liquid and gas migration, making them essential in environmental protection and resource management. This article explores the types of geomembranes, their differences, and their crucial roles in engineering projects.
What are the three types of geomembranes?
The three primary types of geomembranes include:
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Known for its high strength and resistance to chemicals, HDPE geomembranes are commonly used in landfill and containment applications, often complementing Geosynthetic Clay Liners for enhanced performance.
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): More flexible than HDPE, LDPE geomembranes are often used in applications requiring ease of installation, such as pond liners and aquaculture, where Geosynthetic Clay Liners can provide additional sealing benefits.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC geomembranes offer good chemical resistance and flexibility, making them suitable for various containment and environmental applications, frequently paired with Geosynthetic Clay Liners to improve overall system effectiveness.
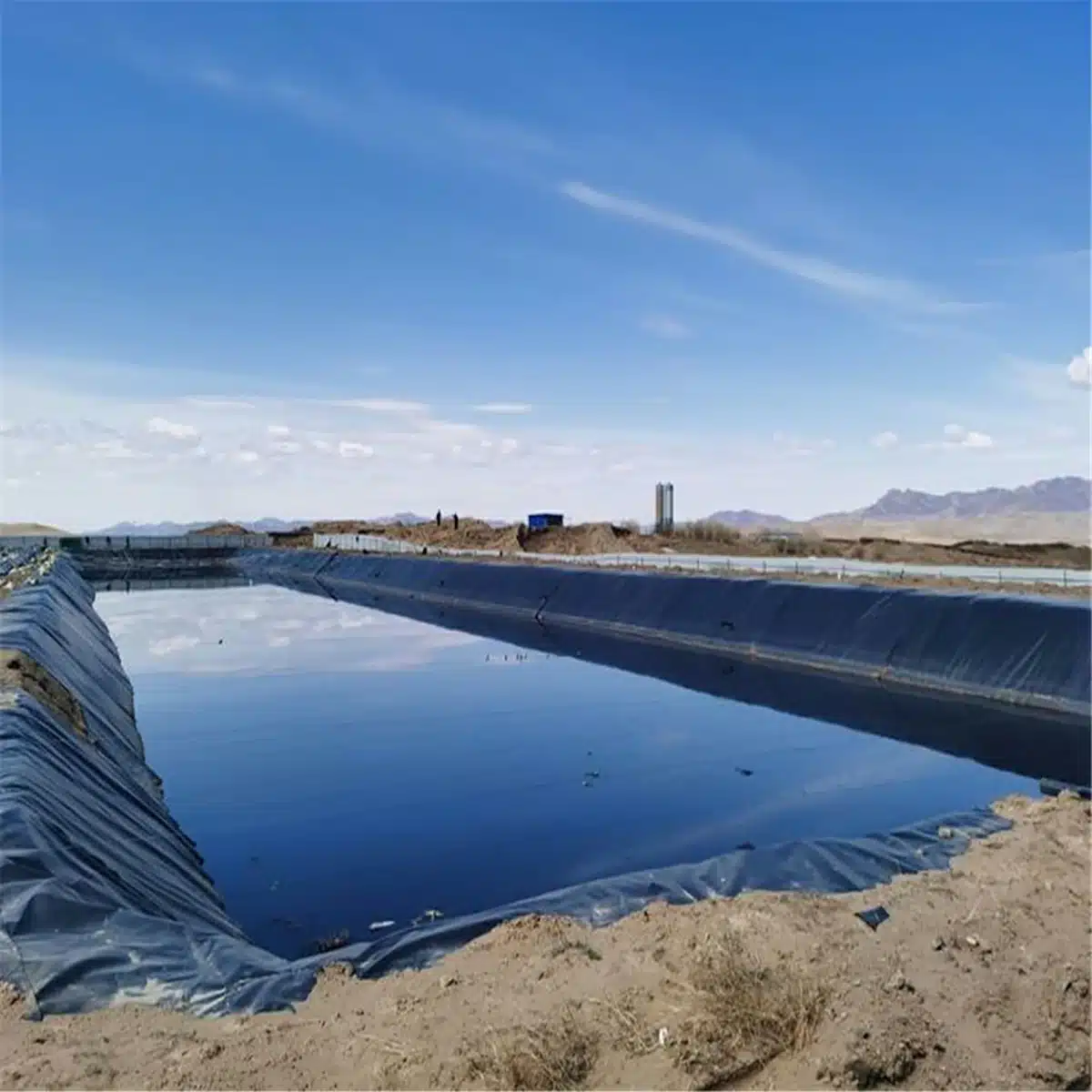

What is the difference between geomembrane and HDPE?
While HDPE is a specific type of geomembrane, the term “geomembrane” encompasses a broader range of materials. HDPE geomembranes are recognized for their robustness, high tensile strength, and resistance to UV radiation and chemicals, whereas PVC geomembranes are flexible and relatively easy to handle, while HDPE geomembranes are tough and non-flexible. In contrast, geomembranes can include other materials, such as LDPE and PVC, each with unique properties suited for different applications. Therefore, all HDPE is geomembrane, but not all geomembranes are HDPE.
What is the difference between GCL and geomembrane?
GCL, or Geosynthetic Clay Liner, is a composite material that consists of a thin layer of bentonite clay between two layers of nonwoven geotextiles. Unlike geomembranes, which are primarily used as impermeable barriers, GCLs combine the impermeable qualities of clay with the durability of synthetic materials. GCLs are often used in landfill liners, where they provide added protection against leakage, whereas geomembranes are typically employed in applications requiring high resistance to various environmental factors.
What is the purpose of a geomembrane?
Geomembranes serve several critical purposes, including:
- Barrier Function: They prevent the migration of liquids and gases, making them ideal for applications in landfills, ponds, and containment structures.
- Environmental Protection: Geomembranes help protect soil and groundwater from contamination by containing hazardous materials.
- Water Management: In applications such as reservoirs and aquaculture, geomembranes help manage water retention and prevent loss.
- Stabilization: Geomembranes can provide stabilization in slopes and embankments, enhancing structural integrity in engineering projects to stabilize the earth and to secure landfills, ensuring containment of hazardous or municipal wastes and their leachates.
Prefabricated geomembranes are vital materials in modern engineering, offering effective solutions for environmental protection and resource management. Understanding the various types of geomembranes, their differences, and their purposes is essential for making informed decisions in construction and land use. With their unique properties and applications, geomembranes continue to play a crucial role in sustainable engineering practices.


Comments
Post a Comment