Geogrids Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Reinforcement and Erosion Prevention
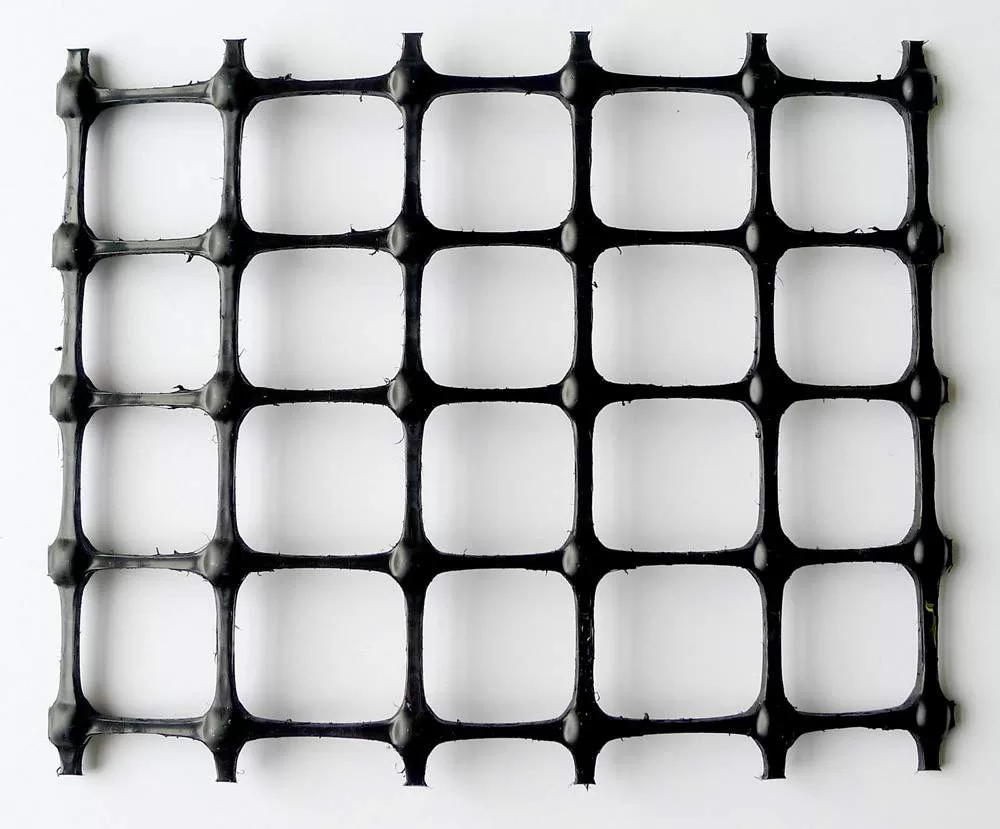
Geogrids are essential materials in modern construction, providing critical soil reinforcement and stability. These grid-like structures, often made from polymers such as polyethylene, are designed to strengthen and stabilize soil by providing a reinforcing structure that interlocks with the soil. When combined with properly sized aggregate fills, geogrids not only improve load distribution but also offer additional benefits like filtration and separation. This article delves into the role of geogrids in enhancing soil stability, addressing key questions and concepts related to their use.
What is a soil stability geogrid?
A soil-stability geogrid is a geosynthetic material specifically designed to reinforce and stabilize soil. It consists of a grid structure that enhances the load-bearing capacity of the soil, making it more resistant to deformation under stress. By interlocking with the aggregate fill, geogrids provide reinforcement, stabilization, and even filtration when used with properly sized aggregate fills, improving the distribution of loads across the surface and preventing issues like soil erosion and structural failure in roads, retaining walls, and slopes.
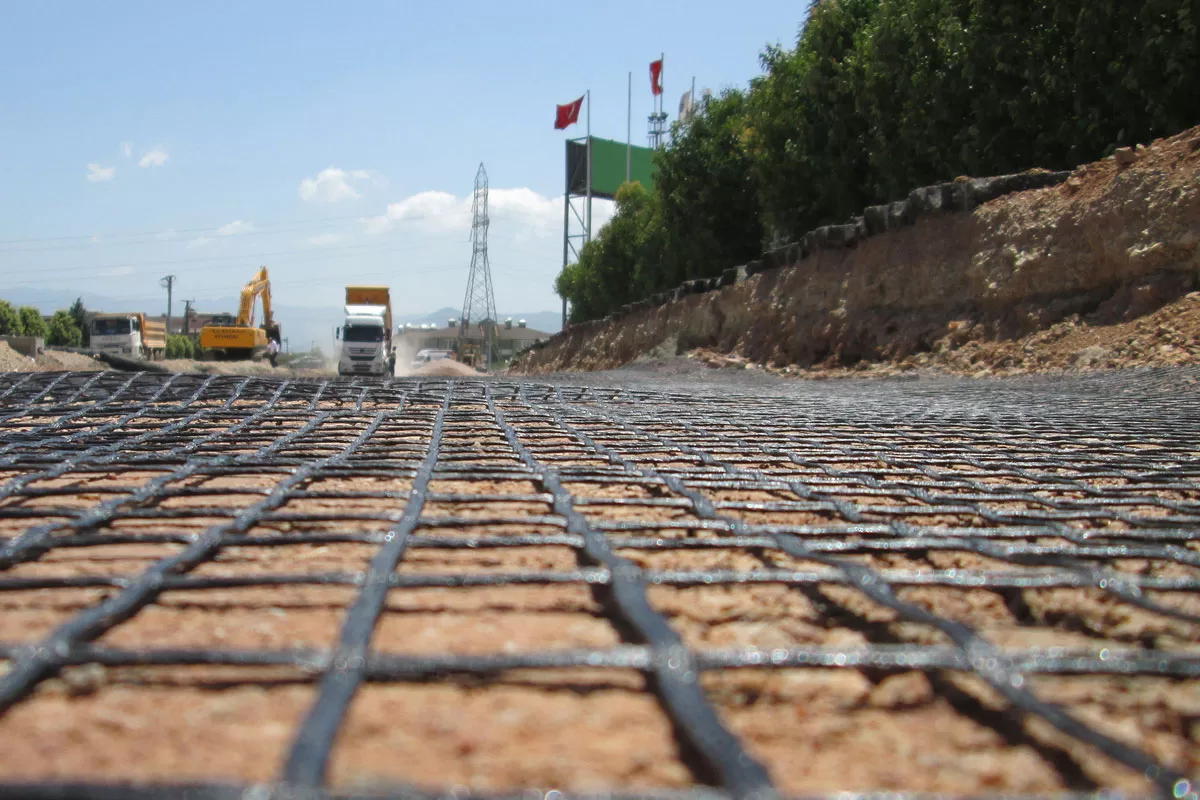

How does a geogrid provide reinforcement, stabilization, and filtration?
Geogrids, used primarily for soil reinforcement, work by interlocking with the surrounding soil and aggregate material. This interlocking action creates a reinforcement layer that distributes loads more evenly, preventing the soil from shifting under pressure. In addition to reinforcement, geogrids also contribute to stabilization by reducing the lateral displacement of soil particles. When used with properly sized aggregate fills, geogrids can provide filtration, allowing water to pass through while retaining soil particles, reducing erosion, and improving drainage.
Where are geogrids primarily used for soil reinforcement?
Geogrids are primarily used in areas where soil reinforcement is crucial, such as in the construction of roads, embankments, retaining walls, and slopes. They help prevent soil erosion, landslides, and structural instability by creating a more resilient foundation that can endure heavy loads. Geogrids are also used in the stabilization of soft soils, enabling the construction of infrastructure on otherwise unsuitable terrain. This makes geogrids an invaluable tool in civil engineering projects that require long-lasting and reliable soil support.
Can geogrids endure heavy loads?
Yes, geogrids are designed to endure heavy loads and provide long-term soil stability, offering numerous sustainability benefits in construction projects. The material used in geogrids, such as high-density polyethylene or polypropylene, is not only highly durable but also resistant to environmental factors like UV exposure and chemical degradation. This strength enables geogrids to withstand the significant pressures exerted by heavy construction vehicles, retaining walls, and road traffic, making them an ideal solution for both temporary and permanent soil reinforcement, while contributing to more sustainable infrastructure development.
Geogrids play a vital role in modern construction by providing reinforcement, stabilization, and filtration in various soil types. When combined with properly sized aggregate fills, they offer an efficient solution for improving soil stability. Geogrids are primarily used for soil reinforcement in applications such as roads, slopes, and retaining walls, where they can endure heavy loads and provide long-term durability. Their versatility and strength make them an essential component in any project requiring enhanced soil stability.


Comments
Post a Comment