Ground Geocell: Strengthening the Foundation of Modern Construction
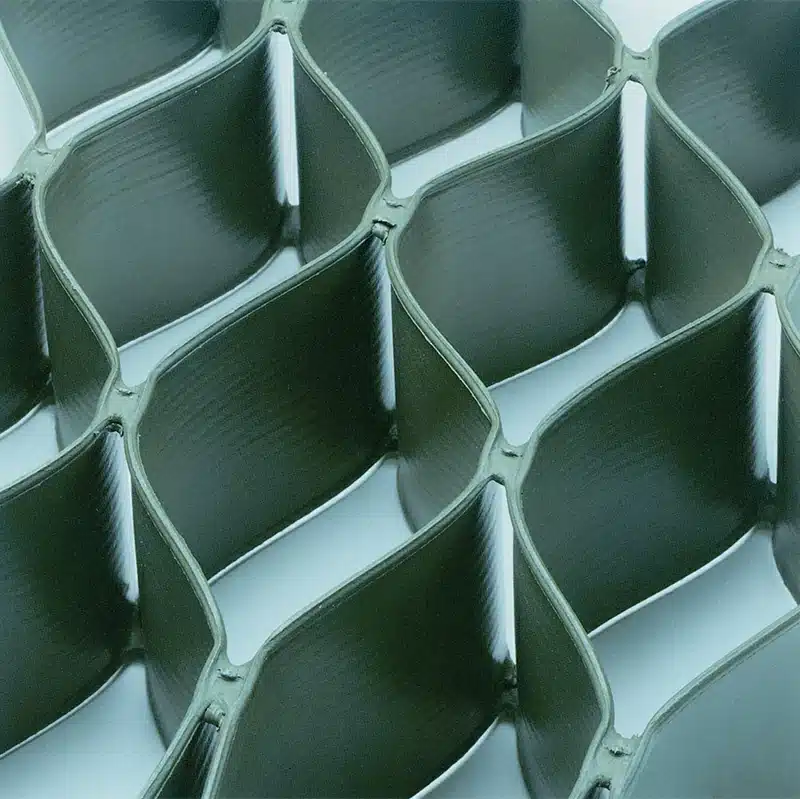
Ground geocells are a versatile and innovative solution for soil stabilization, erosion control, and load distribution in various civil engineering projects. Made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other durable materials, geocells create a honeycomb-like structure that reinforces the ground. By confining soil or other infill materials within the cells, they provide greater stability and load-bearing capacity. This article explores the purpose of geocells, their different types, and their applications, along with the comparison to geogrid solutions.
What is the purpose of geocell?
The primary purpose of ground geocells is to enhance soil stability, providing stabilizing and protection while improving load distribution across various surfaces. By confining materials such as soil, sand, gravel, or even concrete within their cell structure, geocells increase the load-bearing capacity of the surface, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications like roads, railways, and embankments. They also mitigate soil erosion on slopes and riverbanks by providing structural reinforcement to the terrain, preventing runoff and soil displacement.
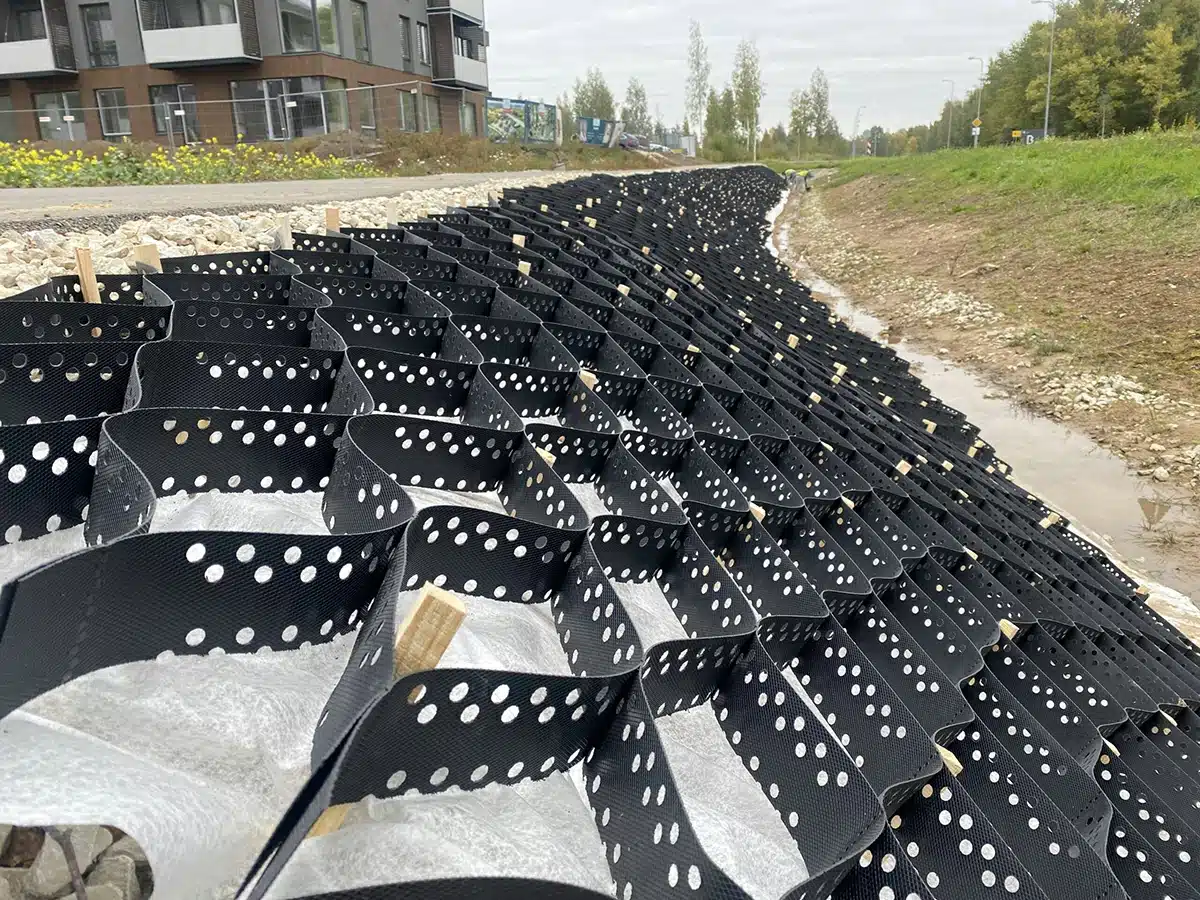

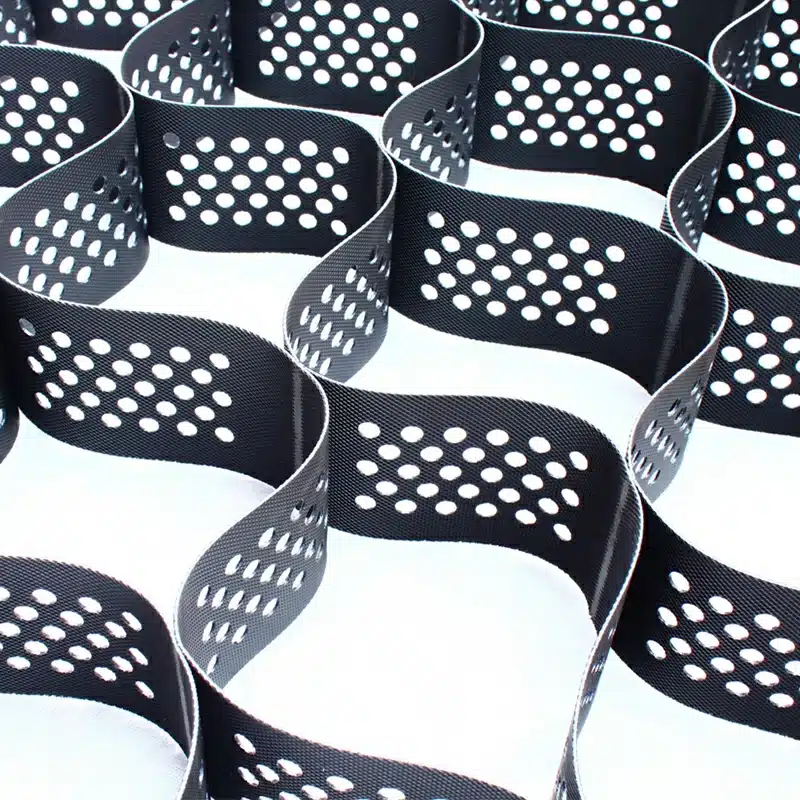
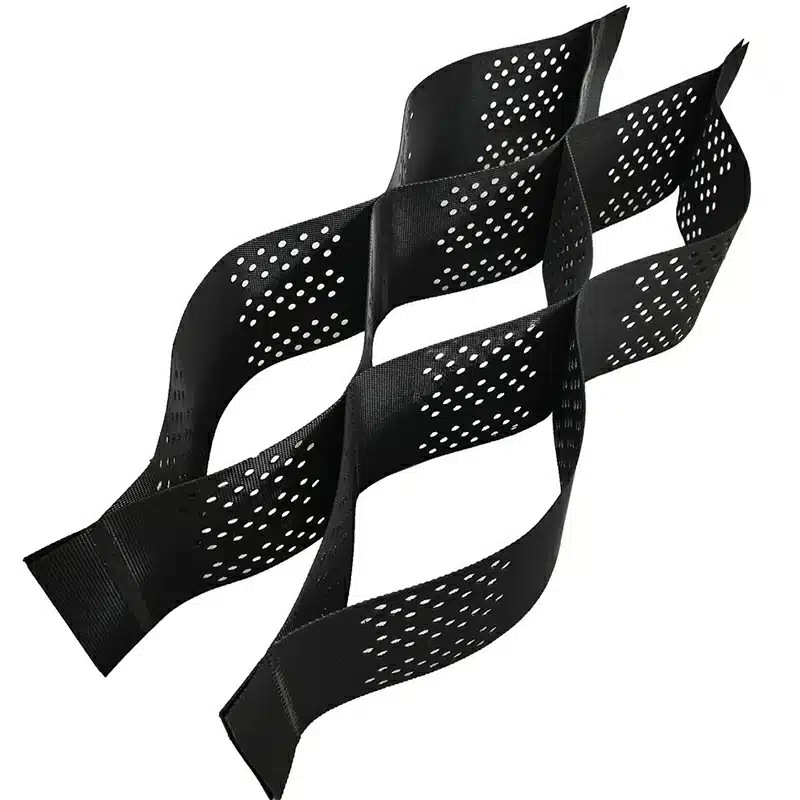
What are the different types of geocells?
Geocells come in different variations, mainly categorized by material composition and design specifics, including non-perforated geocell and perforated geocell:
- HDPE Geocells: These are the most common type of geocells made from high-density polyethylene. They offer excellent strength and durability, suitable for most soil stabilization and erosion control projects, whether you’re using non-perforated geocell and perforated geocell, depending on drainage needs.
- Geocomposite Geocells: These geocells integrate additional layers such as geotextiles or geomembranes to improve filtration and drainage properties, making them ideal for complex projects like landfill covers or water management systems, where both non-perforated geocell and perforated geocell options may be considered.
- Perforated Geocells: These geocells have perforations in their walls, allowing water to pass through, making them ideal for drainage-focused applications like stormwater management and erosion control. In contrast, non-perforated geocell may be better suited for applications requiring maximum containment.
When to use geocell?
Geocells are ideal for projects requiring soil stabilization, slope protection, and load distribution to protect slopes from erosion and help stabilize the surface. They are commonly used in the following scenarios:
- Road and Railway Construction: Geocells reinforce the foundation by distributing loads more evenly, reducing the stress on the subsoil.
- Slope Protection: On steep slopes and embankments, geocells prevent erosion **to protect slopes from erosion and help stabilize the surface** by holding the soil in place and allowing vegetation to grow, which further stabilizes the area.
- Retaining Walls: Geocells provide reinforcement for retaining walls by increasing their load-bearing capacity and preventing collapse.
- Flood and Erosion Control: In flood-prone areas or along riverbanks, geocells help prevent soil displacement and protect the landscape from severe erosion while helping to stabilize the surface.
What is the difference between geogrid and geocell?
While both geogrids and geocells are used in soil stabilization, they differ in structure and function:
- Geogrid: Geogrids are two-dimensional structures made from polymers like polypropylene or polyester. The geogrid is typically two-dimensional and is designed to reinforce soil by providing tensile strength across large surface areas. Geogrids are typically used for load-bearing applications like road reinforcement or slope stabilization, where lateral strength is critical.
- Geocell: Geocells, on the other hand, are three-dimensional and form a honeycomb-like structure that confines infill materials. The geocell is a deep, three-dimensional mesh structure that enhances vertical load distribution and prevents erosion. Geocells are ideal for applications where soil confinement is required, such as in slope protection and erosion control.
Ground geocells are a powerful tool in modern construction, offering solutions for load distribution, soil stabilization, and erosion control. Their versatile applications, from roads to slopes and retaining walls, make them essential for infrastructure projects. By understanding the purpose of geocells, the different types available, and their optimal use, engineers and construction professionals can make informed decisions about when and how to incorporate these innovative materials into their projects. Furthermore, while geogrids and geocells may serve similar purposes, their differences in structure and function allow each to shine in specific applications, enhancing the overall efficiency of construction solutions.


Comments
Post a Comment