How Geotextile Fabric Prevents Soil Erosion and Boosts Soil Stability
Geogrids are essential elements in contemporary retaining wall construction, as they provide reinforcement and enhance the stability of these structures. Their use is particularly vital in areas subject to erosion, heavy loads, or unstable soil conditions, ensuring the longevity and strength of the wall. Whenever you want your hardscape to last and stay structurally sound, the integration of geogrids becomes paramount. This article will explore how geogrids contribute to the structural integrity of retaining walls, their practical applications, and the factors to consider when incorporating them into your project.
When Should You Use Geogrid?
structural stability. It is particularly beneficial in several key situations:
- Heavy Load Support: When the wall must bear substantial loads, such as in landscaping or large civil engineering projects, geogrids provide the necessary reinforcement to maintain stability.
- Weak or Unstable Soil Conditions: If the retaining wall is built on weak or unstable soil, geogrids help distribute the pressure more evenly, preventing the wall from shifting or failing.
- Erosion and Movement Risks: In areas vulnerable to erosion or movement caused by water infiltration or vibrations, geogrids enhance the wall’s resistance to these threats.
- Height Considerations: For walls taller than three to four feet, geogrids are particularly crucial. They ensure the wall meets engineering guidelines and significantly improve its performance.
By integrating geogrids into these scenarios, the structural integrity and longevity of retaining walls are greatly enhanced, reducing the risk of failure.
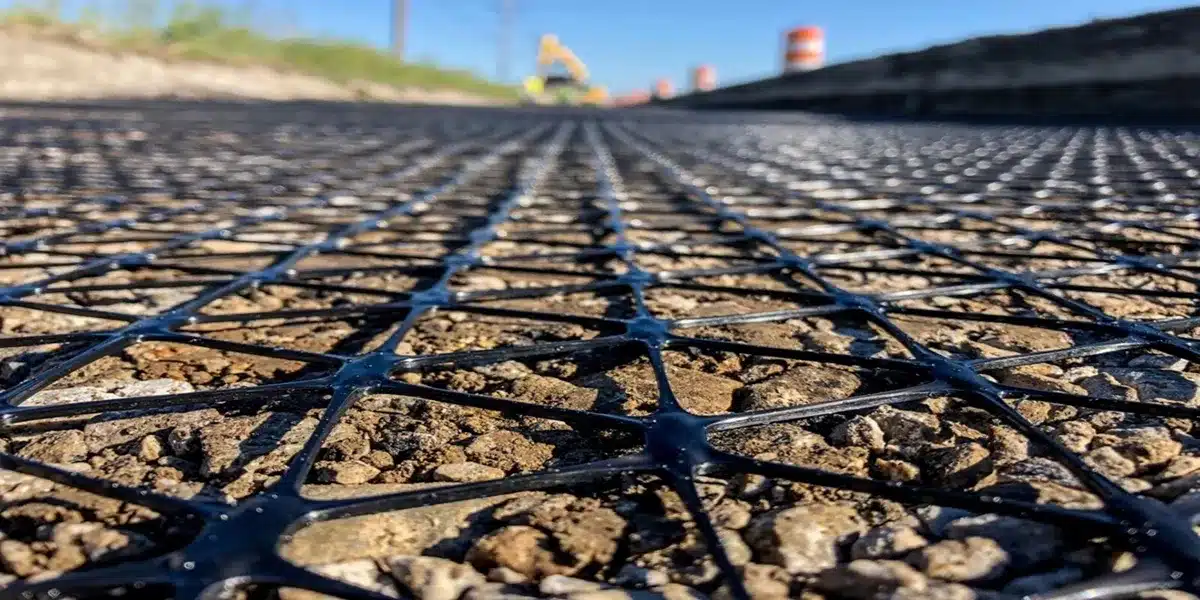

Is Geogrid Necessary for a Retaining Wall?
When constructing retaining walls, it’s essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the project to determine the appropriate use of geogrid reinforcement. Here’s a breakdown:
When to Use Geogrids
- Taller or Load-Bearing Walls: Geogrids are highly recommended for walls that need to support substantial weight. For these types of structures, the reinforcement provided by geogrids enhances stability and durability.
- Challenging Conditions: In areas with unstable soils, high lateral loads, or risk of shifting, geogrids act as a critical reinforcement, ensuring the wall can withstand external forces.
- Complex Retaining Walls: Geogrids provide additional stability for retaining walls that need to resist erosion, vibrations, or movement caused by water infiltration, making them an ideal solution for preventing property damage from collapsing.
When Geogrids May Be Omitted
- Low-Risk, Aesthetic Walls: In residential landscaping projects, where retaining walls are primarily for decorative purposes and not subject to heavy loads or soil movement, geogrids are not typically necessary.
By assessing the specific conditions and purpose of the retaining wall, you can determine whether the use of geogrids is warranted. Geogrids play a crucial role in reinforcing structures and ensuring their long-term stability, especially in more complex or load-bearing projects.
Where Do You Put a Geogrid?
Geogrid is strategically integrated into the body of retaining walls to enhance their structural integrity. Typically, it is placed in layers between the soil and the stone or concrete blocks. The placement of these geogrid layers should be done at regular intervals, ensuring they extend from near the base of the wall upward. This setup maximizes the reinforcement, thereby distributing the weight of the wall more effectively. Furthermore, proper placement of the geogrid is essential not only for weight distribution but also for reducing lateral pressure on the structure. Geogrid should be positioned on the subgrade, either parallel to the road centerline or at right angles, to ensure maximum stability and reinforcement efficiency.
What Are the Benefits of Geogrids?
The integration of geogrids in retaining walls offers a variety of crucial advantages, both structurally and economically:
- Increased Stability: Geogrids anchor the soil behind the wall, preventing it from sliding, tilting, or overturning. This reinforcement is essential in maintaining the wall’s integrity and longevity.
- Improved Load Distribution: By evenly distributing the weight of the wall across the base, geogrids reduce the likelihood of settling or shifting. This load distribution also plays a role in reducing rutting damage, which can occur due to concentrated pressure points.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Geogrids help lower overall construction costs by minimizing the need for expensive materials, such as large stones or concrete supports. Their long-term durability also reduces maintenance expenses.
- Erosion Control: Beyond enhancing the wall’s structural stability, geogrids prevent soil erosion by stabilizing the surrounding soil and promoting vegetation growth. Additionally, they distribute traffic loads within the pavement foundation layers, increase the resilient modulus of the base course, and stabilize the subgrade layer, improving overall pavement performance and extending the lifespan of the retaining wall structure.
Geogrids play an essential role in enhancing the performance and longevity of retaining walls. They are particularly useful in situations where additional reinforcement is required due to unstable soil, heavy loads, or height restrictions. While not always necessary for smaller walls, geogrids offer significant benefits in terms of stability, cost-effectiveness, and erosion control. By understanding when and how to use geogrids, builders can ensure that their retaining walls are strong, durable, and built to last.

Comments
Post a Comment