Uniaxial vs Biaxial Geogrid: Understanding the Key Differences and Industry Applications
In the world of geosynthetics, understanding the distinctions between uniaxial vs biaxial geogrid is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of soil reinforcement and stabilization projects. Both types of geogrids play vital roles in improving load distribution, but their applications differ depending on the nature of the project. This article will explore the differences between uniaxial and biaxial geogrids and provide real-world examples of their successful use.
Uniaxial Geogrids
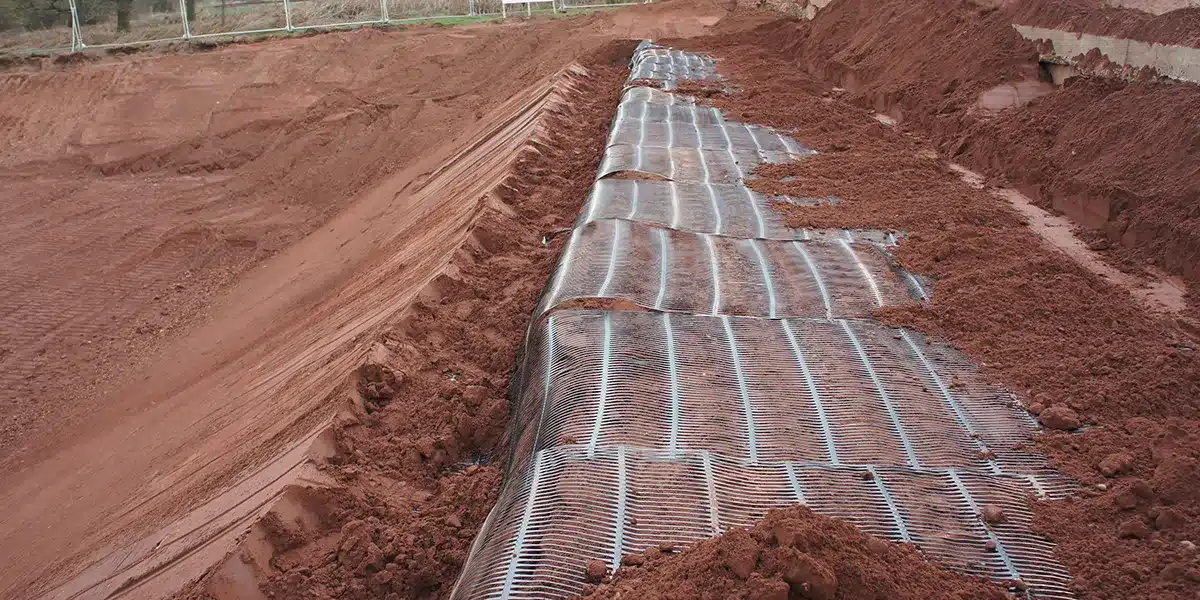

Uniaxial geogrids are designed with strength in one direction and are primarily used in applications where the soil structure requires reinforcement along a single plane, such as in slope stabilization or retaining walls. These geogrids are most effective when placed in conditions where the primary loads are applied in one direction. An example of this can be found in the construction of a highway embankment in the U.S., where uniaxial geogrids were used to reinforce the soil, improving the stability and longevity of the embankment under heavy traffic conditions.
Biaxial Geogrids
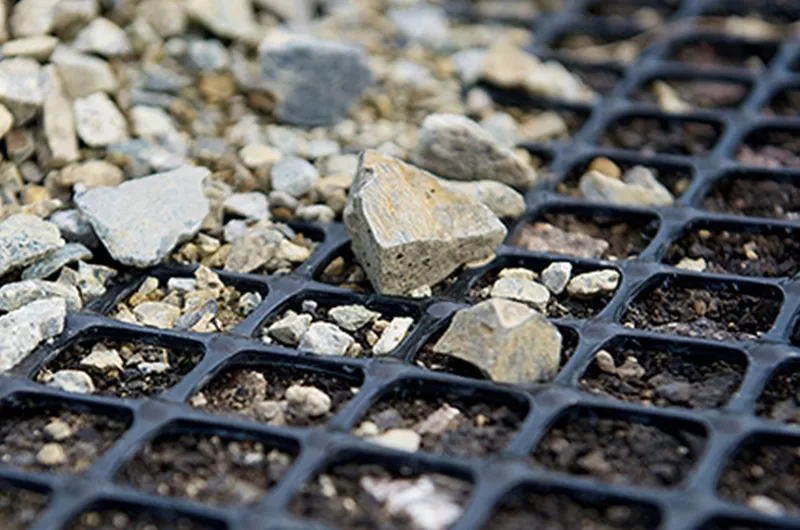

On the other hand, biaxial geogrids provide reinforcement in both horizontal and vertical directions, making them ideal for use in applications where load distribution occurs across multiple planes. This type of geogrid is frequently used in the construction of roads, pavements, and even landfill bases. A notable case study involved the use of biaxial geogrids in a large-scale road construction project in the Middle East, where they were instrumental in increasing the load-bearing capacity of the foundation and extending the lifespan of the roadway.
Key Differences Between Uniaxial and Biaxial Geogrids
The key differences between uniaxial vs biaxial geogrid come down to their design and the type of loads they are intended to manage. While uniaxial geogrids excel in reinforcing structures that are exposed to unidirectional forces, biaxial geogrids offer superior performance in multi-directional load situations, providing versatility in a range of civil engineering applications.
In conclusion, both uniaxial and biaxial geogrids have unique characteristics that make them essential to specific projects in the geosynthetics industry. Understanding the distinctions between these two types of geogrids allows engineers and contractors to select the appropriate material for soil reinforcement, ensuring the long-term success of their projects. For professionals in the industry, grasping the nuances of uniaxial vs biaxial geogrid technology can lead to more informed decision-making and better project outcomes.


Comments
Post a Comment