Geocell Soil Stabilizer: Enhancing Soil Strength in Civil Engineering Projects
In the world of civil engineering, the use of geocell soil stabilizer technology has become a game-changer for improving soil strength and stability in challenging environments. This article explores the key aspects of geocell soil stabilizer systems, answering common questions related to their application, benefits, and performance.
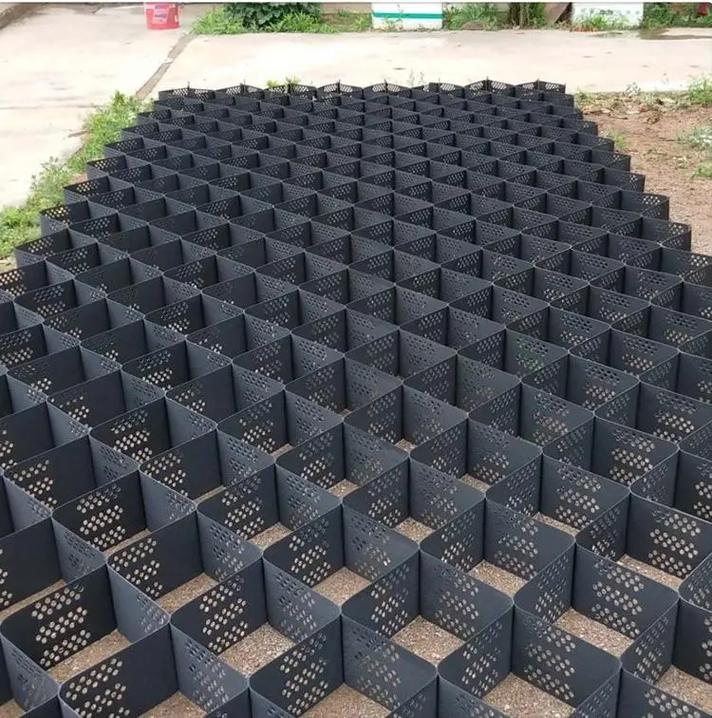

What is a geocell soil stabilizer, and how does it work?
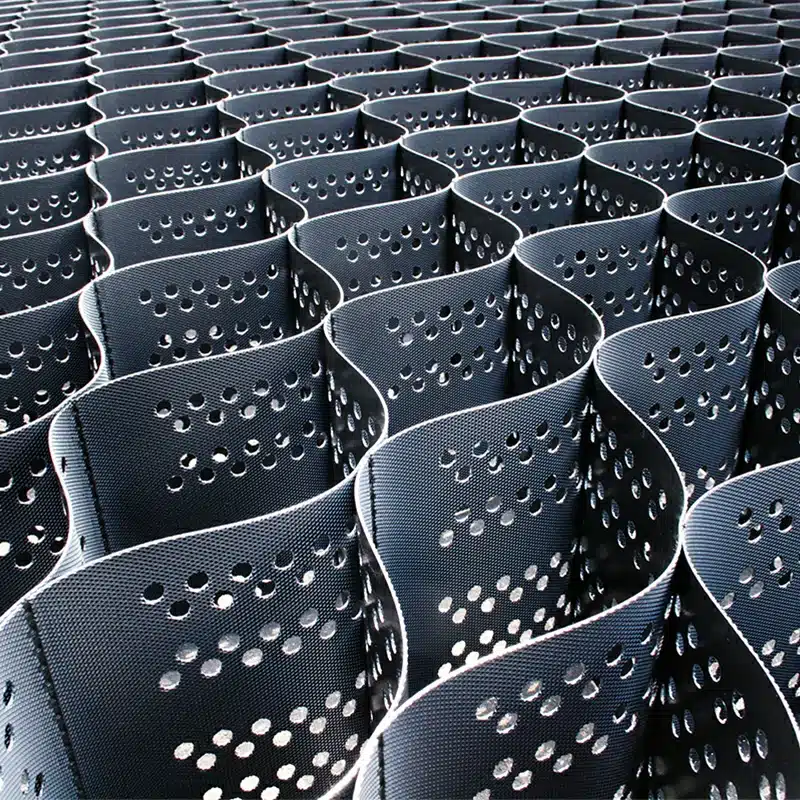
A geocell soil stabilizer is a three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structure made of polymer materials designed to improve the load-bearing capacity of weak or loose soils. It works by confining the soil particles, preventing them from shifting under pressure, which helps to create a more stable foundation for construction projects. The geocells are filled with soil or aggregate materials, which distribute the load across a larger area, increasing stability and reducing settlement.
What are the primary benefits of using a geocell soil stabilizer?
The primary benefits of a geocell soil stabilizer include:
- Increased load-bearing capacity: It enhances the strength of the soil, making it capable of supporting heavier loads.
- Cost-effectiveness: By stabilizing existing soil, it reduces the need for expensive materials like crushed stone or concrete.
- Reduced erosion: The confinement provided by geocells helps to prevent soil erosion in areas prone to washouts.
- Environmental sustainability: Using locally available materials to fill geocells minimizes the environmental impact of construction projects.
These benefits make geocell soil stabilizer systems a preferred choice for infrastructure projects such as roads, railways, and embankments.
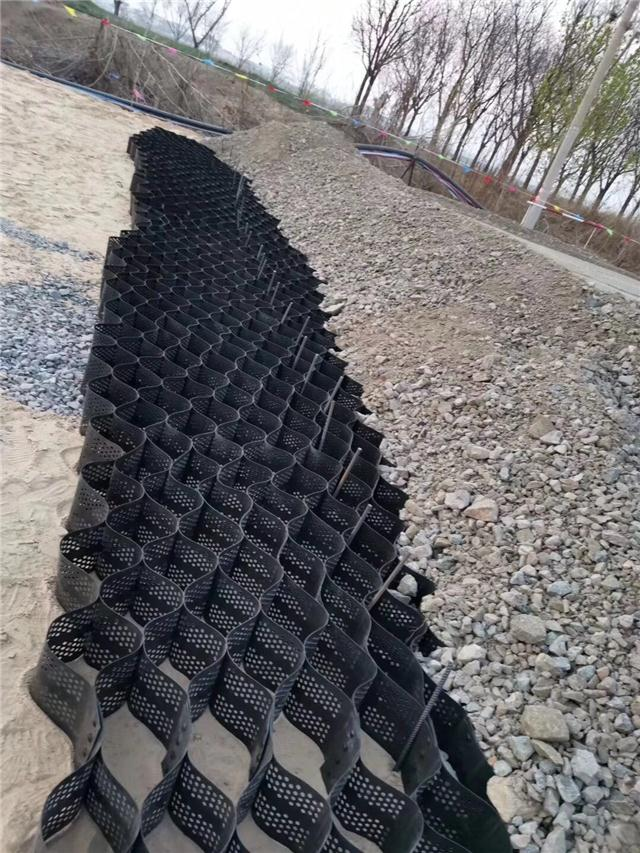

How does the performance of a geocell soil stabilizer compare to traditional soil stabilization methods?
When compared to traditional methods, such as deep soil mixing or chemical stabilization, geocell soil stabilizer systems offer several advantages:
- Improved performance: Geocells provide enhanced performance in terms of load distribution and soil confinement, especially in areas with weak or loose soil.
- Faster installation: Geocell systems are quicker to install compared to more labor-intensive traditional methods.
- Longer lifespan: The polymer materials used in geocells are durable and resistant to environmental degradation, ensuring long-term stability.
According to Industry Research, the use of geocell systems can improve soil strength by up to 60% compared to traditional stabilization techniques. This makes them a highly effective solution for construction projects in challenging soil conditions.
What are some real-world applications of geocell soil stabilizer in construction?
- Road and railway embankments: Geocells help prevent settling and maintain the integrity of the roadbed or track foundation.·
- Slope protection: Geocells are used for stabilizing slopes and preventing erosion, especially in areas with steep inclines.
- Pavement foundations: By enhancing soil strength, geocells provide a stable foundation for pavements, reducing cracking and rutting over time.
In fact, geocell soil stabilizer applications have been implemented in large-scale projects such as highway construction in mountainous regions and airport runway expansions in areas with soft soil. According to Civil Engineering Research Journal, these projects have demonstrated a 30% increase in stability and a 50% reduction in material costs.
In conclusion, the integration of geocell soil stabilizer systems into civil engineering projects offers numerous advantages, from increased soil stability to cost savings and environmental sustainability. As technology continues to advance, the role of geocells in shaping the future of construction becomes increasingly vital.


Comments
Post a Comment