Geonet vs Geotextile: Understanding Their Roles in Modern Geosynthetics
In civil engineering and environmental applications, understanding the differences between geonet vs geotextile is crucial for selecting the right material. These geosynthetics play distinct yet complementary roles in drainage, separation, and soil reinforcement systems.
What is a geonet used for?

A geonet is primarily used for drainage applications. Composed of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), it consists of a net-like structure that allows fluids to flow easily in a plane. Geonets are commonly used in landfill drainage systems, roadways, and retaining walls to divert water and prevent pressure buildup.
- Industry data shows that geonets can achieve flow rates up to 30 times higher than granular drainage layers.
- — Source: Geosynthetics Research Institute (GRI), 2023
Their high compressive strength and durability make them ideal for long-term drainage performance under heavy loads.
What is the difference between geotextile and Geonet?
The core difference lies in function and structure:
- Geotextiles are permeable fabrics made from polypropylene or polyester. They are used for separation, filtration, reinforcement, and erosion control.
- Geonets, on the other hand, are three-dimensional nets used exclusively for planar fluid drainage.
For example, in landfill caps, geotextiles are often placed above geonets to filter fine particles, preventing clogging and ensuring effective drainage.
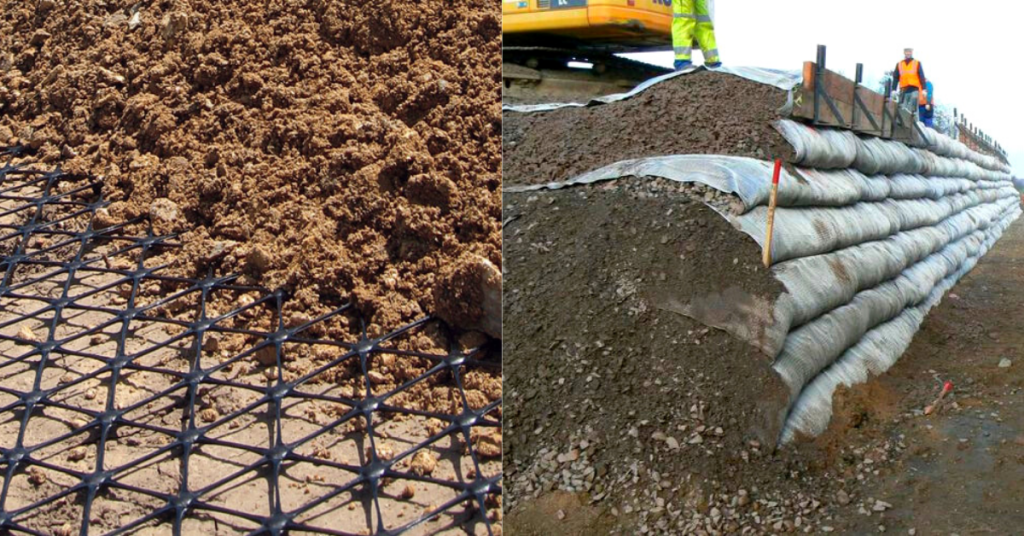

How do engineers decide between geonet and geotextile for a project?
Selection depends on project goals and site conditions. If the goal is to allow water to pass through while retaining soil, engineers will likely choose geotextiles. However, if the requirement is high-volume water flow within a layer, geonets are preferred.
In many modern projects, both are used together: a geotextile for filtration, layered above a geonet for drainage. This combination has become common in landfill leachate collection systems and green roof drainage layers.
- In 2022, over 60% of large infrastructure drainage systems used combined geonet and geotextile layers.
- — Source: International Geosynthetics Society (IGS), 2023
Are there performance standards for geonets and geotextiles?
Yes. Both materials are subject to strict industry testing and classification. For example:
- Geonets are tested for in-plane flow rate under pressure (ASTM D4716).
- Geotextiles are evaluated for permittivity, puncture resistance, and tensile strength (ASTM D4491, D4632, etc.).
- High-quality geonets must maintain at least 70% of their initial flow capacity after 10,000 hours of compressive loading.
- — Source: ASTM and ISO Geosynthetics Standards Review, 2024
Specifiers must ensure compatibility with soil type, chemical exposure, and expected mechanical loads.
In conclusion, knowing the distinction between geonet vs geotextile allows engineers to design more efficient and durable systems. Whether used individually or in tandem, these geosynthetics are key components in sustainable infrastructure design.
Geonet vs geotextile comparisons will continue to shape best practices across geotechnical applications.

Comments
Post a Comment