The Power of Geocomposite Drainage Layers: Enhancing Infrastructure Sustainability
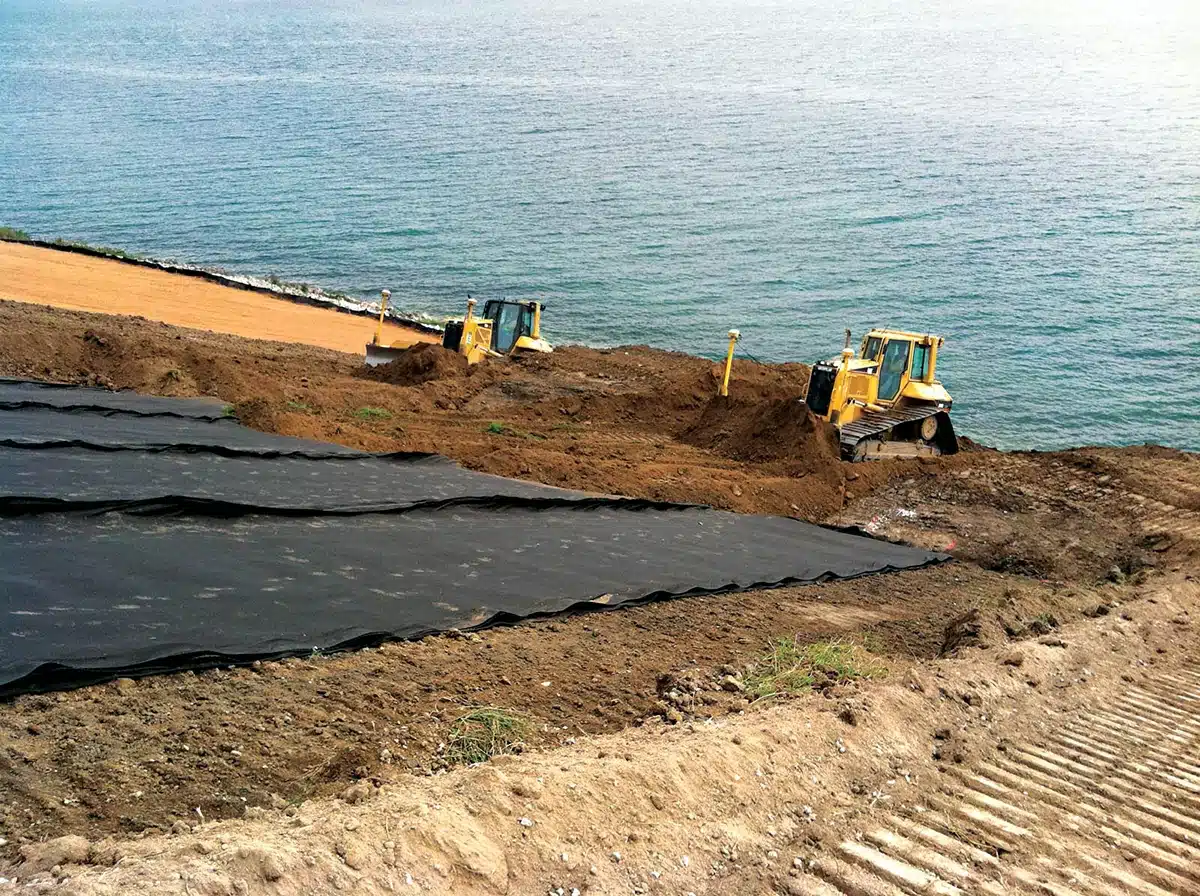
Geocomposite drainage layers stand as indispensable components in fortifying infrastructure against water-related challenges. These specialized layers, crafted with a blend of geotextiles, drainage cores, and filtration systems, serve a pivotal role in managing water flow efficiently. By seamlessly redirecting and filtering liquids, these layers prevent waterlogging, curb hydrostatic pressure, and safeguard structures from potential water-induced damage. Whether in road construction, landscaping, or environmental containment projects, geocomposite drainage layers offer a robust solution, enhancing the resilience and longevity of vital infrastructure.

What is a geocomposite drainage layer?
A geocomposite drainage layer is a versatile material combining geotextiles, drainage cores, and filtration systems. This specialized structure efficiently manages water flow, exhibiting outstanding drainage capacities in diverse applications. Its innovative design not only facilitates efficient water collection, filtration, and conveyance but also extends its functionality to collect and convey both liquids and gases. Minimizing hydrostatic pressure effectively safeguards construction projects against water-related damage.
What is a geocomposite liner?
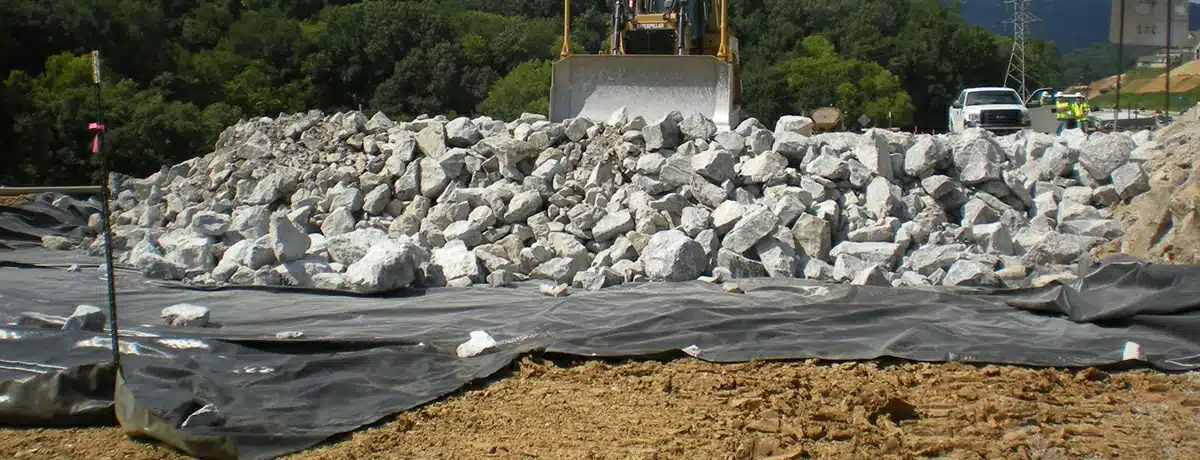
A geocomposite liner, tailored for containment applications like landfills or reservoirs, is a specialized solution engineered to prevent the seepage of liquids or gases. This liner consists of a tri-planar geonet heat-laminated on both sides with a nonwoven geotextile, combining impermeable membranes, geotextiles, and drainage cores. Its purpose is to create a robust barrier system that effectively shields the surrounding environment from potential contaminants, ensuring superior structural integrity and environmental protection.

What is the purpose of geocomposite?
Geocomposite materials serve a multifaceted role, pivotal in optimizing infrastructure longevity by expertly managing water flow. Their core functions encompass separation, drainage, filtration, and reinforcement. These materials efficiently redirect water, thwarting waterlogging, curbing hydrostatic pressure, and circumventing potential water-induced harm. In a spectrum of construction ventures—be it roadways, retaining walls, landfills, or athletic fields—geocomposites play a pivotal role, ensuring efficient water management critical for upholding structural stability.
How does geocomposite work?
Geocomposites, crafted from a blend of geotextiles, geomembranes, geogrids, or other geosynthetic materials, serve specific roles in civil engineering, environmental, and geotechnical contexts. Here’s an overview of their functionality:
- Reinforcement: Geocomposites bolster soil, retaining walls, embankments, or slopes by evenly dispersing loads and bolstering stability. For instance, a geocomposite integrated with geogrids can fortify the bearing capacity of feeble soils.
- Filtration: These composites enable the passage of liquid through the geotextiles into the geonet, diverting it away to a collection point while halting soil particle migration. This filtering mechanism aids drainage systems, preserving soil integrity and permitting water flow to minimize erosion.
- Separation: Within road construction or civil engineering ventures, geocomposites act as a barrier between distinct soil or aggregate layers, thwarting amalgamation and upholding structure integrity.
- Drainage: Tailored geocomposites are adept at draining excess water from soils or structures. They facilitate fluid movement while preventing soil particle obstruction, ensuring efficient liquid flow into the geonet and towards a designated collection area.
- Erosion Control: Utilized in erosion control, geocomposites stabilize soil and impede surface erosion. Their design allows water to traverse, averting soil particle displacement and safeguarding against erosion.
Geocomposites’ efficacy hinges on their design specifics, constituent materials, and intended applications. Their versatility in civil engineering presents solutions for challenges concerning soil stability, water regulation, and diverse construction projects.


Comments
Post a Comment